作者:bwner@浙銀網絡安全創新實驗室
本文為作者投稿,Seebug Paper 期待你的分享,凡經采用即有禮品相送! 投稿郵箱:paper@seebug.org
前言
最近在學習 IoT 相關漏洞利用,打算先學習一下 Qiling 框架,為后續的漏洞利用文章做鋪墊。 Qiling 框架是基于 unicorn 的多架構平臺模擬執行框架,提供的仿真環境很全面,能夠在模擬執行的基礎上提供統一的分析 API,這個A PI 包括插樁分析、快照、系統調用和API劫持等操作。在2021年JOANSIVION提供了兩個QilingLab能夠針對Qiling框架各種操作進行學習的程序,并提供了相應的writeup。他提供的 writeup 是 arm 架構的,因此本文以 x86_64 架構為基礎,在他的文章上進行相應補充。程序下載地址放在了文末參考鏈接中。
時隔兩年,Qiling 框架進行了很多更新與改動,我在完成 QilingLab 的過程中發現高版本的 Qiling 存在問題,因此從代碼審計的角度入手,分析并提出解決方案,如果曾經分析過 QilingLab 的朋友可以直接跳到 Challenge 10 部分。本文將以最為基礎的視角來陪著大家從 0 到 1 學習 Qiling 框架,希望大家看完能有所收獲。
首先下載Qiling:
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/qilingframework/qiling.git # 使用 --recurse-submodules 遞歸下載模塊,rootfs是單獨更新的項目使用版本為最新版:
> pip show qiling
Name: qiling
Version: 1.4.5
Summary: Qiling is an advanced binary emulation framework that cross-platform-architecture可以看到 QilingLab 提供的11個挑戰如下:
Welcome to QilingLab.
Here is the list of challenges:
Challenge 1: Store 1337 at pointer 0x1337.
Challenge 2: Make the 'uname' syscall return the correct values.
Challenge 3: Make '/dev/urandom' and 'getrandom' "collide".
Challenge 4: Enter inside the "forbidden" loop.
Challenge 5: Guess every call to rand().
Challenge 6: Avoid the infinite loop.
Challenge 7: Don't waste time waiting for 'sleep'.
Challenge 8: Unpack the struct and write at the target address.
Challenge 9: Fix some string operation to make the iMpOsSiBlE come true.
Challenge 10: Fake the 'cmdline' line file to return the right content.
Challenge 11: Bypass CPUID/MIDR_EL1 checks.整體分析
運行一下程序,可以看到輸出了挑戰的所有題目:
> ./qilinglab-x86_64
Welcome to QilingLab.
Here is the list of challenges:
Challenge 1: Store 1337 at pointer 0x1337.
Challenge 2: Make the 'uname' syscall return the correct values.
Challenge 3: Make '/dev/urandom' and 'getrandom' "collide".
Challenge 4: Enter inside the "forbidden" loop.
Challenge 5: Guess every call to rand().
Challenge 6: Avoid the infinite loop.
Challenge 7: Don't waste time waiting for 'sleep'.
Challenge 8: Unpack the struct and write at the target address.
Challenge 9: Fix some string operation to make the iMpOsSiBlE come true.
Challenge 10: Fake the 'cmdline' line file to return the right content.
Challenge 11: Bypass CPUID/MIDR_EL1 checks.
Checking which challenge are solved...
Note: Some challenges will results in segfaults and infinite loops if they aren't solved.
[1] 8036 segmentation fault (core dumped) ./qilinglab-x86_64先調用Qiling仿真環境運行一下:
from qiling import *
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = ["qilinglab-x86_64"]
rootfs = "rootfs/x8664_linux"
ql = Qiling(path, rootfs)
ql.run()發現報錯:
unicorn.unicorn.UcError: Invalid memory read (UC_ERR_READ_UNMAPPED)接下來進行分析無法運行的原因,按照出題人所說需要解決第一個挑戰才能正常進入。首先查看一下文件信息,可以看到程序使用小端順序,符號表未裁剪:
> readelf -h qilinglab-x86_64
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: DYN (Shared object file)
Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0xa80
Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 15840 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 56 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 9
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 29
Section header string table index: 28> file -L qilinglab-x86_64
qilinglab-x86_64: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, BuildID[sha1]=76164e6b494c1af9d9f746e2dc7d3663cc23525c, not stripped拖到IDA里看一下函數流程,main函數:
; Attributes: bp-based frame
; int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
public main
main proc near
var_10= qword ptr -10h
var_4= dword ptr -4
; __unwind {
push rbp
mov rbp, rsp
sub rsp, 10h
mov [rbp+var_4], edi
mov [rbp+var_10], rsi
mov eax, 0
call start
mov eax, 0
leave
retn
; } // starts at 15CA
main endp可以看到跳轉到start,查看一下start偽代碼:
unsigned __int64 start()
{
int v0; // eax
int i; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-20h]
int v3; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
int v4; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
int v5; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
int v6; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
int v7; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
int v8; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
int v9; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
int v10; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
int v11; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
int v12; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
char v13[11]; // [rsp+Dh] [rbp-13h] BYREF
char v14[11]; // [rsp+Eh] [rbp-12h] BYREF
char v15[11]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v16; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v16 = __readfsqword(0x28u); // __readfsqword指令的參數是一個偏移量,0x28u是一個無符號整數常量,值為0x28,即40,表示從FS寄存器中的偏移量為40的地址開始讀取64位數據。
for ( i = 0; i < 11; ++i )
v13[i] = 0;
printf("Welcome to QilingLab.\nHere is the list of challenges:");
printf("\nChallenge 1: Store 1337 at pointer 0x1337.");
printf("\nChallenge 2: Make the 'uname' syscall return the correct values.");
printf("\nChallenge 3: Make '/dev/urandom' and 'getrandom' \"collide\".");
printf("\nChallenge 4: Enter inside the \"forbidden\" loop.");
printf("\nChallenge 5: Guess every call to rand().");
printf("\nChallenge 6: Avoid the infinite loop.");
printf("\nChallenge 7: Don't waste time waiting for 'sleep'.");
printf("\nChallenge 8: Unpack the struct and write at the target address.");
printf("\nChallenge 9: Fix some string operation to make the iMpOsSiBlE come true.");
printf("\nChallenge 10: Fake the 'cmdline' line file to return the right content.");
printf("\nChallenge 11: Bypass CPUID/MIDR_EL1 checks.");
puts(
"\n"
"\n"
"Checking which challenge are solved...\n"
"Note: Some challenges will results in segfaults and infinite loops if they aren't solved.");
challenge1(v13);
v3 = checker(v13, 0LL);
challenge2(v14);
v4 = checker(v13, 1LL) + v3;
challenge3(&v14[1]);
v5 = checker(v13, 2LL) + v4;
challenge4(v15);
v6 = checker(v13, 3LL) + v5;
challenge5(&v15[1]);
v7 = checker(v13, 4LL) + v6;
challenge6(&v15[2]);
v8 = checker(v13, 5LL) + v7;
challenge7(&v15[3]);
v9 = checker(v13, 6LL) + v8;
challenge8(&v15[4]);
v10 = checker(v13, 7LL) + v9;
challenge9(&v15[5]);
v11 = checker(v13, 8LL) + v10;
challenge10(&v15[6]);
v12 = checker(v13, 9LL) + v11;
challenge11(&v15[7]);
v0 = checker(v13, 10LL);
printf("\nYou solved %d/%d of the challenges\n", (unsigned int)(v0 + v12), 11LL);
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v16;
}查看調用的checker函數偽代碼,可以知道當檢查到問題已解決時返回1:
__int64 __fastcall checker(__int64 a1, int a2)
{
__int64 result; // rax
if ( *(_BYTE *)(a2 + a1) ) ; 檢查數組a1中下標為a2的元素是否為0,非0返回1
{
printf("\nChallenge %d: SOLVED", (unsigned int)(a2 + 1));
result = 1LL;
}
else
{
printf("\nChallenge %d: NOT SOLVED", (unsigned int)(a2 + 1));
result = 0LL;
}
return result;
}我們梳理一下函數邏輯:循環初始化數組v13所有元素為0,如果完成對應挑戰就會改變v13對應數組的值,再用checker進行一次檢查v13數組元素是否為0.再將checker返回值傳遞給變量,再加到下一次的檢查結果上。這個過程不斷重復,最后將累加起來的值輸出到"\nYou solved %d/%d of the challenges\n"。
Challenge 1: 內存數據修改
拖到IDA里看一下 challenge 1 匯編代碼:
.text:0000000000000B8A public challenge1
.text:0000000000000B8A challenge1 proc near ; CODE XREF: start+123↓p
.text:0000000000000B8A
.text:0000000000000B8A var_18 = qword ptr -18h ; 分配quadword類型的局部變量var_18位于[rbp-18h]的位置
.text:0000000000000B8A var_C = dword ptr -0Ch ; qword 8字節,dword 4字節
.text:0000000000000B8A var_8 = qword ptr -8
.text:0000000000000B8A
.text:0000000000000B8A ; __unwind {
.text:0000000000000B8A push rbp
.text:0000000000000B8B mov rbp, rsp
.text:0000000000000B8E mov [rbp+var_18], rdi ; [rbp-18h], rdi 此處rdi值為指向v13的指針
.text:0000000000000B92 mov [rbp+var_8], 1337h
.text:0000000000000B9A mov rax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000000000000B9E mov eax, [rax] ; 將內存地址1337h的值傳遞給eax
.text:0000000000000BA0 mov [rbp+var_C], eax
.text:0000000000000BA3 cmp [rbp+var_C], 539h ; cmp jnz: 不相等就跳轉loc_BB3進行retn (539h = 1337)
.text:0000000000000BAA jnz short loc_BB3
.text:0000000000000BAC mov rax, [rbp+var_18]
.text:0000000000000BB0 mov byte ptr [rax], 1 ; 將值為1的字節寫入存儲在rax所指向的內存地址中
.text:0000000000000BB3
.text:0000000000000BB3 loc_BB3: ; CODE XREF: challenge1+20↑j
.text:0000000000000BB3 nop
.text:0000000000000BB4 pop rbp
.text:0000000000000BB5 retn
.text:0000000000000BB5 ; } // starts at B8A可以看出我們需要讓內存地址1337h處的值為1337才能讓cmp判斷相等,rdi傳入的是數組地址對應數組首個元素地址,相等后調整rdi地址處的值為1,這也符合后續被checker函數檢查數組后進行的一系列操作。
.text:0000000000000B8E mov [rbp+var_18], rdi
...
.text:0000000000000BAC mov rax, [rbp+var_18]
.text:0000000000000BB0 mov byte ptr [rax], 1challenge 1 對應的偽代碼如下:
_BYTE *__fastcall challenge1(_BYTE *a1)
{
_BYTE *result; // rax
result = (_BYTE *)*(unsigned int *)((char *)&loc_1335 + 2); // 標識符loc_xxxx通常用于表示一個內存地址或常量值
if ( *(_DWORD *)((char *)&loc_1335 + 2) == 1337 )
{
result = a1;
*a1 = 1;
}
return result;
}在Qiling中編寫字節序列常用有以下方式,我選用的是pack16。
ql.mem.write(0x1000, b'\x41\x42\x43') # 手動輸入
ql.pack(">I", 0x12345678) # 函數調用將返回一個4字節的大端序字節序列,其中包含整數值 0x12345678 的二進制表示。
# ">I"參數指定了這個字節序列的格式,其中">"表示大端序,"<"表示小端序,"I"表示一個32位無符號整數。
ql.pack16(0x1234) # 這個函數專門用于16位整數writeup 1
根據前面的分析可以得到 challenge 1 writeup:
from qiling import *
def challenge1(ql):
ql.mem.map(0x1000, 0x1000, info='[challenge1]')
# 為地址范圍?[0x1000, 0x2000) 映射了一塊內存,第一個參數0x1000是映射的起始地址,第二個參數0x1000是映射的大小,映射的大小必須是頁大小的倍數,這里的頁大小是 Qiling模擬器的默認頁大小,4096字節。info是對這部分內存做的一個標記,后續Qiling如果想接著使用的話就可以用這個標記來定位。
ql.mem.write(0x1337, ql.pack16(1337))
# 將整數值 1337 轉換為一個16位字節序列寫入內存地址 0x1337 所指定的內存位置,小端輸入
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = ["qilinglab-x86_64"]
rootfs = "rootfs/x8664_linux"
ql = Qiling(path, rootfs)
challenge1(ql)
ql.run()運行上面的腳本,可以看到 challenge 1 已經解決:
Challenge 11: Bypass CPUID/MIDR_EL1 checks.
Checking which challenge are solved...
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x54) = 0x54
Note: Some challenges will results in segfaults and infinite loops if they aren't solved.
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x5a) = 0x5a
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x1) = 0x1
[=] uname(buf = 0x80000000db70) = 0x0
Challenge 1: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
[=] openat(fd = 0xffffff9c, path = 0x555555555698, flags = 0x0, mode = 0x0) = -0x2 (ENOENT)
[=] read(fd = 0xffffffff, buf = 0x80000000dce0, length = 0x20) = -0x9 (EBADF)
[=] read(fd = 0xffffffff, buf = 0x80000000dcdf, length = 0x1) = -0x9 (EBADF)
[=] close(fd = 0xffffffff) = -0x1 (EPERM)
[=] getrandom(buf = 0x80000000dd00, buflen = 0x20, flags = 0x1) = 0x20
Challenge 2: NOT SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x18) = 0x18
Challenge 3: NOT SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x18) = 0x18
[=] time() = 0x64704df9
Challenge 4: NOT SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x18) = 0x18如果我們想使用Qiling進行遠程調試的話,應該怎么做?
我們在使用qemu配合IDA進行遠程調試時,需要使用下面的qemu-arm-static:
sudo chroot ./ ./qemu-arm-static -g 12345 ./bin/httpd查了一下qiling文檔,調試qiling的仿真程序需要在腳本中添加下面的代碼:
ql.debugger = 'gdb:0.0.0.0:12345'接著設置一下IDA的gdb debugger,斷點在入口函數處,
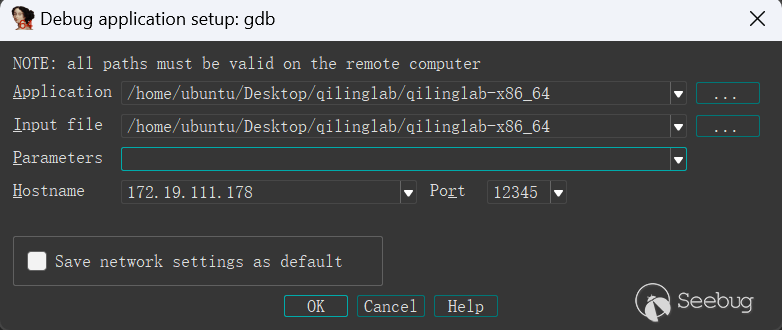
運行添加dbg后的腳本:
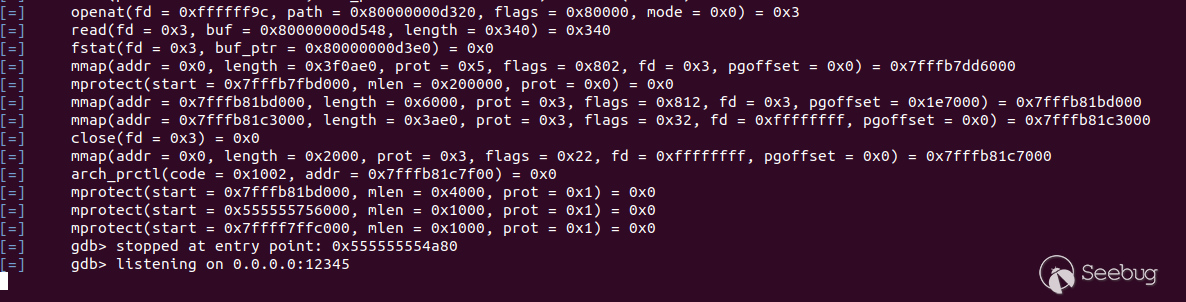
運行后報錯:
ValueError: '/home/ubuntu/Desktop/qilinglab/qilinglab-x86_64' does not start with '/home/ubuntu/Desktop/qilinglab/rootfs/x8664_linux'Qiling對于報錯的提示都挺好的,這里需要將qilinglab-x86_64放置到指定的rootfs目錄(我這里是使用的rootfs/x8664_linux作為rootfs目錄)下運行,復制后更改一下程序運行的路徑,更改后的代碼如下:
from qiling import *
def challenge1(ql):
ql.mem.map(0x1000, 0x1000, info='[challenge1]')
ql.mem.write(0x1337, ql.pack16(1337))
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = ["rootfs/x8664_linux/qilinglab-x86_64"]
rootfs = "rootfs/x8664_linux"
ql = Qiling(path, rootfs)
challenge1(ql)
ql.debugger = 'gdb:0.0.0.0:12345'
ql.run()可以看到程序已經可以遠程調試了:
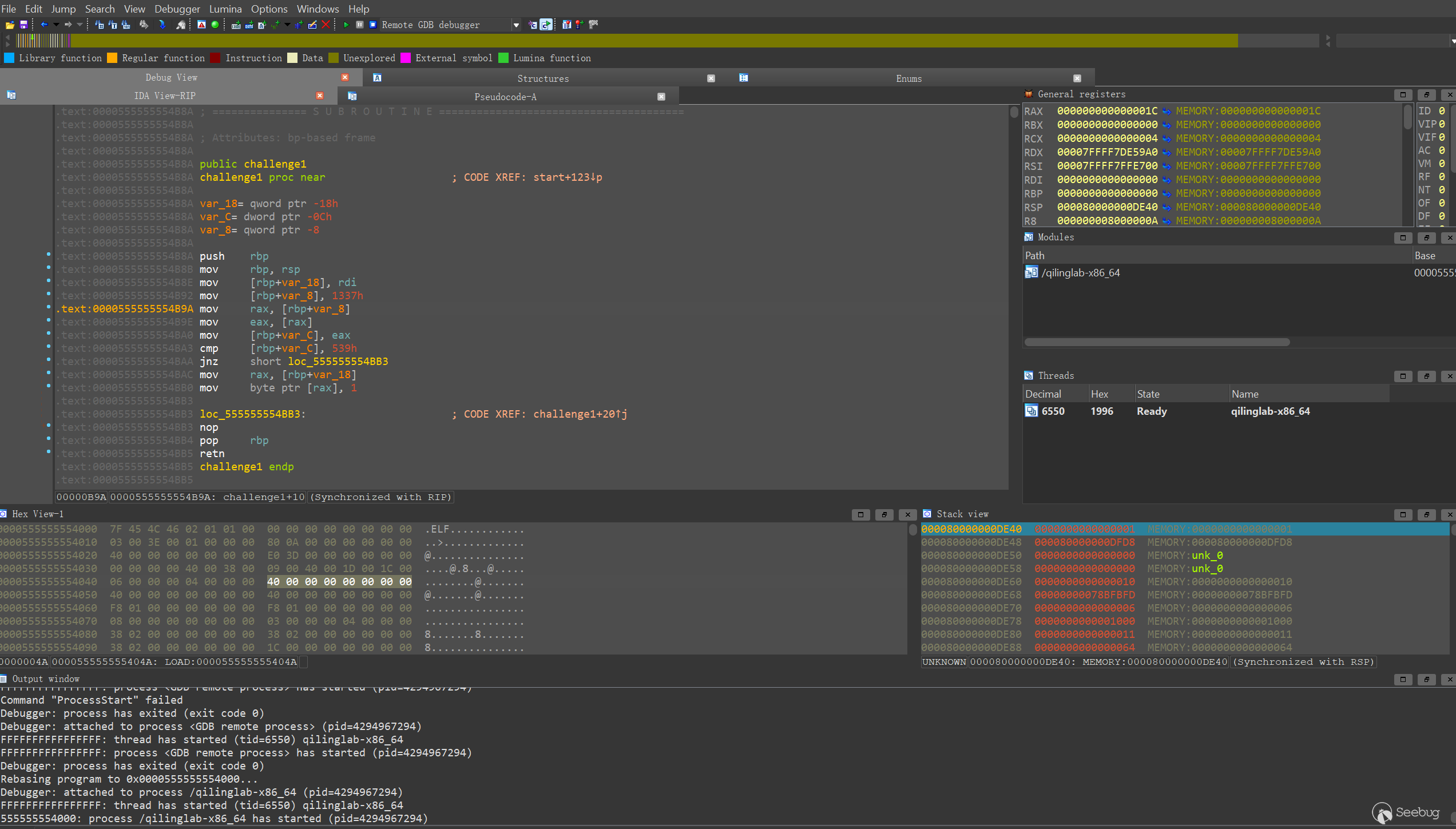
Challenge 2: hook系統調用
Challenge 2: Make the 'uname' syscall return the correct values.
查看challenges 2 匯編代碼:
.text:0000555555554BB6 public challenge2
.text:0000555555554BB6 challenge2 proc near ; CODE XREF: start+147↓p
.text:0000555555554BB6
.text:0000555555554BB6 var_1D8 = qword ptr -1D8h
.text:0000555555554BB6 var_1D0 = dword ptr -1D0h
.text:0000555555554BB6 var_1CC = dword ptr -1CCh
.text:0000555555554BB6 var_1C8 = dword ptr -1C8h
.text:0000555555554BB6 var_1C4 = dword ptr -1C4h
.text:0000555555554BB6 name = utsname ptr -1C0h
.text:0000555555554BB6 s = byte ptr -3Ah
.text:0000555555554BB6 var_32 = word ptr -32h
.text:0000555555554BB6 var_30 = byte ptr -30h
.text:0000555555554BB6 var_18 = qword ptr -18h
.text:0000555555554BB6
.text:0000555555554BB6 push rbp
.text:0000555555554BB7 mov rbp, rsp
.text:0000555555554BBA push rbx
.text:0000555555554BBB sub rsp, 1D8h
.text:0000555555554BC2 mov [rbp+var_1D8], rdi
.text:0000555555554BC9 mov rax, fs:28h ; 從Segment fs(用于TLS)對應的內存段,偏移量40h處取一個值,把這個值加載到rax寄存器
.text:0000555555554BD2 mov [rbp+var_18], rax
.text:0000555555554BD6 xor eax, eax ; 清零eax寄存器,更新零標志位ZF = 1(表示eax為0)
.text:0000555555554BD8 lea rax, [rbp+name] ; 將[rbp+name]的地址傳給rax
.text:0000555555554BDF mov rdi, rax ; name
.text:0000555555554BE2 call _uname
.text:0000555555554BE7 test eax, eax ; 不修改eax的內容,只更新標志位
.text:0000555555554BE9 jz short loc_555555554BFC ; ZF=1,則轉移到目的地址
.text:0000555555554BEB lea rdi, s ; "uname"
.text:0000555555554BF2 call _perror ; _perror() 用于打印錯誤信息
.text:0000555555554BF7 jmp loc_555555554D13
.text:0000555555554BFC ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555554BFC
.text:0000555555554BFC loc_555555554BFC: ; CODE XREF: challenge2+33↑j
.text:0000555555554BFC mov rax, cs:qword_55555555567E
.text:0000555555554C03 mov qword ptr [rbp+s], rax
.text:0000555555554C07 movzx eax, cs:word_555555555686
.text:0000555555554C0E mov [rbp+var_32], ax
.text:0000555555554C12 mov rax, cs:qword_555555555688
.text:0000555555554C19 mov rdx, cs:qword_555555555690
.text:0000555555554C20 mov qword ptr [rbp+var_30], rax
.text:0000555555554C24 mov qword ptr [rbp+var_30+8], rdx
.text:0000555555554C28 mov [rbp+var_1D0], 0
.text:0000555555554C32 mov [rbp+var_1CC], 0
.text:0000555555554C3C jmp short loc_555555554C6D
.text:0000555555554C3E ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555554C3E
.text:0000555555554C3E loc_555555554C3E: ; CODE XREF: challenge2+CF↓j
.text:0000555555554C3E mov eax, [rbp+var_1C8]
.text:0000555555554C44 cdqe
.text:0000555555554C46 movzx edx, [rbp+rax+name.sysname]
.text:0000555555554C4E mov eax, [rbp+var_1C8]
.text:0000555555554C54 cdqe
.text:0000555555554C56 movzx eax, [rbp+rax+s]
.text:0000555555554C5B cmp dl, al
.text:0000555555554C5D jnz short loc_555555554C66
.text:0000555555554C5F add [rbp+var_1D0], 1
.text:0000555555554C66
.text:0000555555554C66 loc_555555554C66: ; CODE XREF: challenge2+A7↑j
.text:0000555555554C66 add [rbp+var_1C8], 1
.text:0000555555554C6D
.text:0000555555554C6D loc_555555554C6D: ; CODE XREF: challenge2+86↑j
.text:0000555555554C6D mov eax, [rbp+var_1C8]
.text:0000555555554C73 movsxd rbx, eax
.text:0000555555554C76 lea rax, [rbp+s]
.text:0000555555554C7A mov rdi, rax ; s
.text:0000555555554C7D call _strlen
.text:0000555555554C82 cmp rbx, rax ; 相等,則ZF=1, CF=0, OF=0
; 小于,則ZF=0, CF=1, OF=0
; 大于,則ZF=0, CF=0, OF=0
.text:0000555555554C85 jb short loc_555555554C3E ; 前一條指令執行的結果為小于則跳轉
.text:0000555555554C87 jmp short loc_555555554CB8 ; 此處跳出循環
.text:0000555555554C89 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555554C89
.text:0000555555554C89 loc_555555554C89: ; CODE XREF: challenge2+11A↓j
.text:0000555555554C89 mov eax, [rbp+var_1C4]
.text:0000555555554C8F cdqe
.text:0000555555554C91 movzx edx, [rbp+rax+name.version]
.text:0000555555554C99 mov eax, [rbp+var_1C4]
.text:0000555555554C9F cdqe
.text:0000555555554CA1 movzx eax, [rbp+rax+var_30]
.text:0000555555554CA6 cmp dl, al
.text:0000555555554CA8 jnz short loc_555555554CB1
.text:0000555555554CAA add [rbp+var_1CC], 1
.text:0000555555554CB1
.text:0000555555554CB1 loc_555555554CB1: ; CODE XREF: challenge2+F2↑j
.text:0000555555554CB1 add [rbp+var_1C4], 1
.text:0000555555554CB8
.text:0000555555554CB8 loc_555555554CB8: ; CODE XREF: challenge2+D1↑j
.text:0000555555554CB8 mov eax, [rbp+var_1C4]
.text:0000555555554CBE movsxd rbx, eax ; 將eax寄存器中的32位符號擴展為64位,并將結果存儲到rbx寄存器中
.text:0000555555554CC1 lea rax, [rbp+var_30]
.text:0000555555554CC5 mov rdi, rax ; s
.text:0000555555554CC8 call _strlen
.text:0000555555554CCD cmp rbx, rax
.text:0000555555554CD0 jb short loc_555555554C89
.text:0000555555554CD2 mov ebx, [rbp+var_1D0]
.text:0000555555554CD8 lea rax, [rbp+s]
.text:0000555555554CDC mov rdi, rax ; s
.text:0000555555554CDF call _strlen
.text:0000555555554CE4 cmp rbx, rax
.text:0000555555554CE7 jnz short loc_555555554D13
.text:0000555555554CE9 mov ebx, [rbp+var_1CC]
.text:0000555555554CEF lea rax, [rbp+var_30]
.text:0000555555554CF3 mov rdi, rax ; s
.text:0000555555554CF6 call _strlen
.text:0000555555554CFB cmp rbx, rax
.text:0000555555554CFE jnz short loc_555555554D13
.text:0000555555554D00 cmp [rbp+var_1D0], 5
.text:0000555555554D07 jbe short loc_555555554D13
.text:0000555555554D09 mov rax, [rbp+var_1D8]
.text:0000555555554D10 mov byte ptr [rax], 1
.text:0000555555554D13
.text:0000555555554D13 loc_555555554D13: ; CODE XREF: challenge2+41↑j
.text:0000555555554D13 ; challenge2+131↑j ...
.text:0000555555554D13 mov rax, [rbp+var_18]
.text:0000555555554D17 xor rax, fs:28h
.text:0000555555554D20 jz short loc_555555554D27
.text:0000555555554D22 call ___stack_chk_fail
.text:0000555555554D27 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555554D27
.text:0000555555554D27 loc_555555554D27: ; CODE XREF: challenge2+16A↑j
.text:0000555555554D27 add rsp, 1D8h
.text:0000555555554D2E pop rbx
.text:0000555555554D2F pop rbp
.text:0000555555554D30 retn
.text:0000555555554D30 challenge2 endp正確的運行邏輯: challenge2 -> loc_555555554BFC -> loc_555555554C6D -> loc_555555554CB8 -> loc_555555554D13 -> loc_555555554D27
對應偽代碼:
unsigned __int64 __fastcall challenge2(_BYTE *a1)
{
unsigned int v2; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-1D0h]
int v3; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-1CCh]
int v4; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-1C8h]
int v5; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-1C4h]
struct utsname name; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-1C0h] BYREF
char s[10]; // [rsp+1A6h] [rbp-3Ah] BYREF
char v8[24]; // [rsp+1B0h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v9; // [rsp+1C8h] [rbp-18h]
v9 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
if ( uname(&name) )
{
perror("uname");
}
else
{
strcpy(s, "QilingOS");
strcpy(v8, "ChallengeStart");
v2 = 0;
v3 = 0;
while ( v4 < strlen(s) )
{
if ( name.sysname[v4] == s[v4] )
++v2;
++v4;
}
while ( v5 < strlen(v8) )
{
if ( name.version[v5] == v8[v5] )
++v3;
++v5;
}
if ( v2 == strlen(s) && v3 == strlen(v8) && v2 > 5 )
*a1 = 1;
}
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v9;
}第一個if判斷:
if ( uname(&name) )
{
perror("uname");
}uname(&name) 是一個系統調用函數,它的作用是獲取當前系統的名稱和版本信息,并將這些信息存儲到?struct utsname?類型的結構體變量?name?中,name 使用struct utsname name;聲明 ,如果成功獲取的話函數返回值為0,就可以進入else了。else中我們最后需要執行*a1 = 1,這里面有兩個循環進行字符串逐個判斷,如果相同就能在最后的if判斷中讓*a1 = 1。此處我們需要了解uname的結構體,uname的結構為:
struct utsname {
char sysname[65];
char nodename[65];
char release[65];
char version[65];
char machine[65];
char domainname[65];
};我們需要讓name.sysname等于"QilingOS",name.version等于"ChallengeStart"。
出題人提供了源碼,可以看到源碼的邏輯跟分析的一致:
void challenge2(char *check) {
unsigned int i, j, k, l;
struct utsname name;
char qiling_OS[10];
char chall_start[24];
if ( uname(&name) ) {
perror("uname");
}
else {
strcpy(qiling_OS, "QilingOS");
strcpy(chall_start, "ChallengeStart");
i = 0;
j = 0;
while ( k < strlen(qiling_OS) ) {
if ( name.sysname[k] == qiling_OS[k] )
++i;
++k;
}
while ( l < strlen(chall_start) ) {
if ( name.version[l] == chall_start[l] )
++j;
++l;
}
if ( i == strlen(qiling_OS) && j == strlen(chall_start) && i > 5 )
*check = 1;
}
}根據上述分析,我們需要hook系統調用uname。在Qiling中有四種hook方式,這四個方式都是常量:
- QL_INTERCEPT.EXIT:在系統調用執行完成之后立即執行hook函數
- QL_INTERCEPT.ENTER:在系統調用執行之前執行hook函數
- QL_INTERCEPT.EXIT_TREE:在系統調用執行完成并返回后,執行完其他所有系統調用的hook函數之后再執行當前系統調用的hook函數
- QL_INTERCEPT.EXIT_ALL:在系統調用執行完成并返回后,執行所有系統調用的hook函數
為了使用上面的hook方式,需要使用 from qiling.const import * 導入Qiling模擬器中的常量。
系統調用返回結構體型數據時,會將結構體的地址存放在寄存器rdi中,因此我們需要使用 ql.arch.regs.rdi得到rdi中存儲的uname地址。
writeup 2
writeup:
from qiling import *
from qiling.const import * #?導入Qiling模擬器中的常量
def my_uname_on_exit_hook(ql, *args):
rdi = ql.arch.regs.rdi
print(f"utsname address: {hex(rdi)}") # utsname address: 0x80000000db50
ql.mem.write(rdi, b'QilingOS\x00')
ql.mem.write(rdi + 65 * 3, b'ChallengeStart\x00') # 000080000000DC13
def challenge2(ql):
# 使用QL_INTERCEPT.EXIT在系統調用執行完成之后立即執行hook函數,ql.os.set_syscall 使用方法在官方文檔 Hijack 部分
ql.os.set_syscall("uname", my_uname_on_exit_hook, QL_INTERCEPT.EXIT)
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = ["rootfs/x8664_linux/qilinglab-x86_64"]
rootfs = "rootfs/x8664_linux"
ql = Qiling(path, rootfs)
# 記得加上challenge1
challenge2(ql)
ql.run()用IDA看一下運行腳本后rdi指向的sysname和version,可以看到已經按照我們的腳本進行了修改:
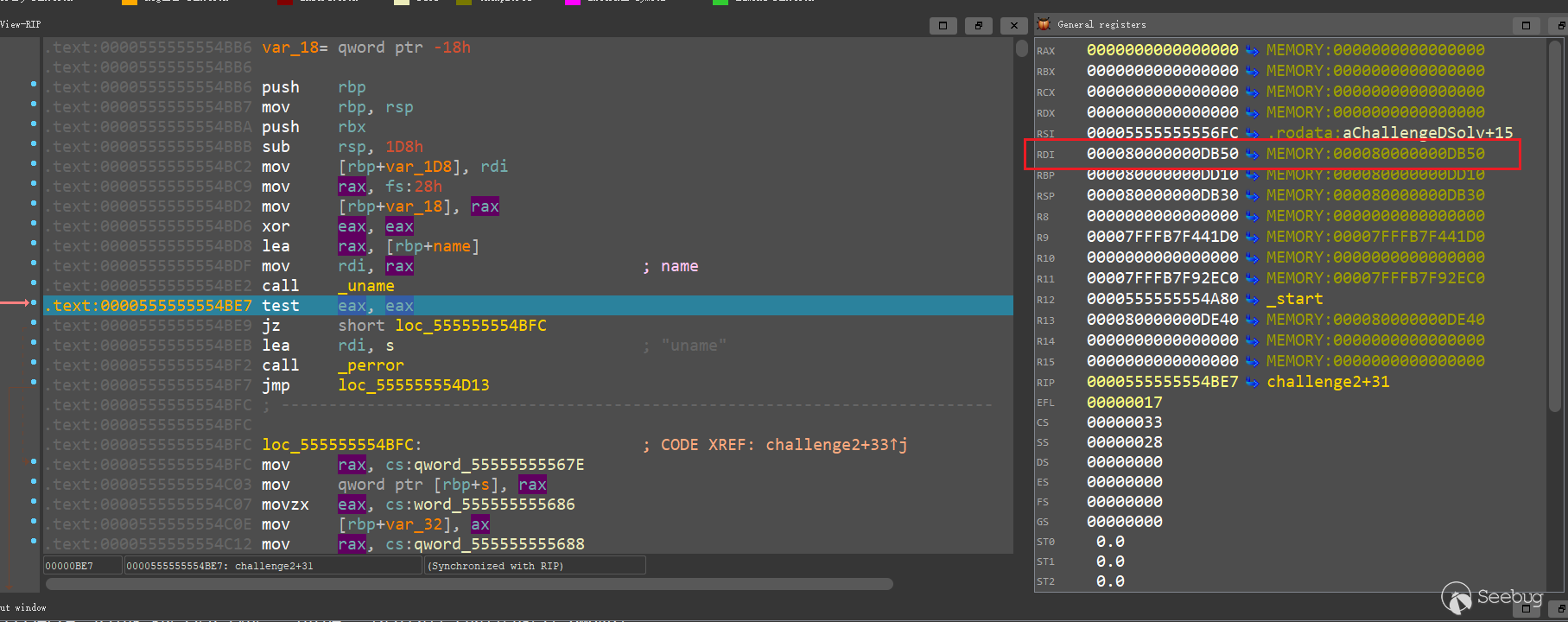
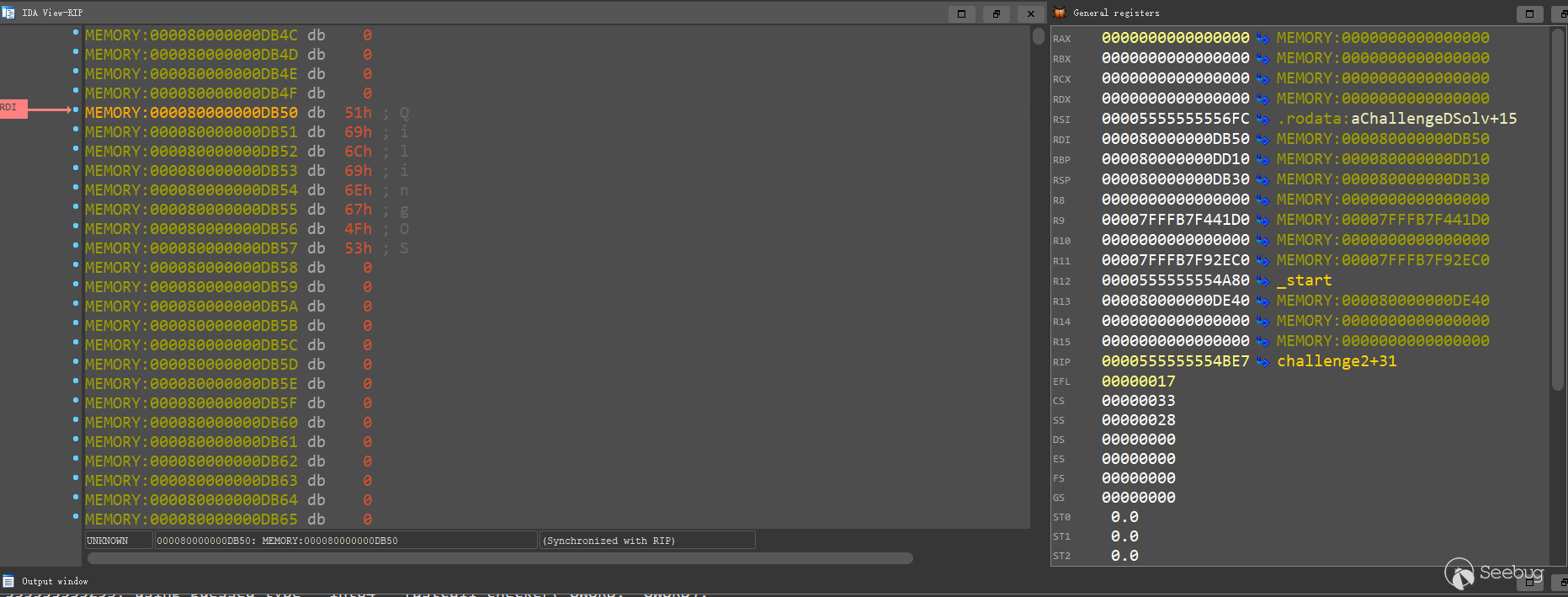
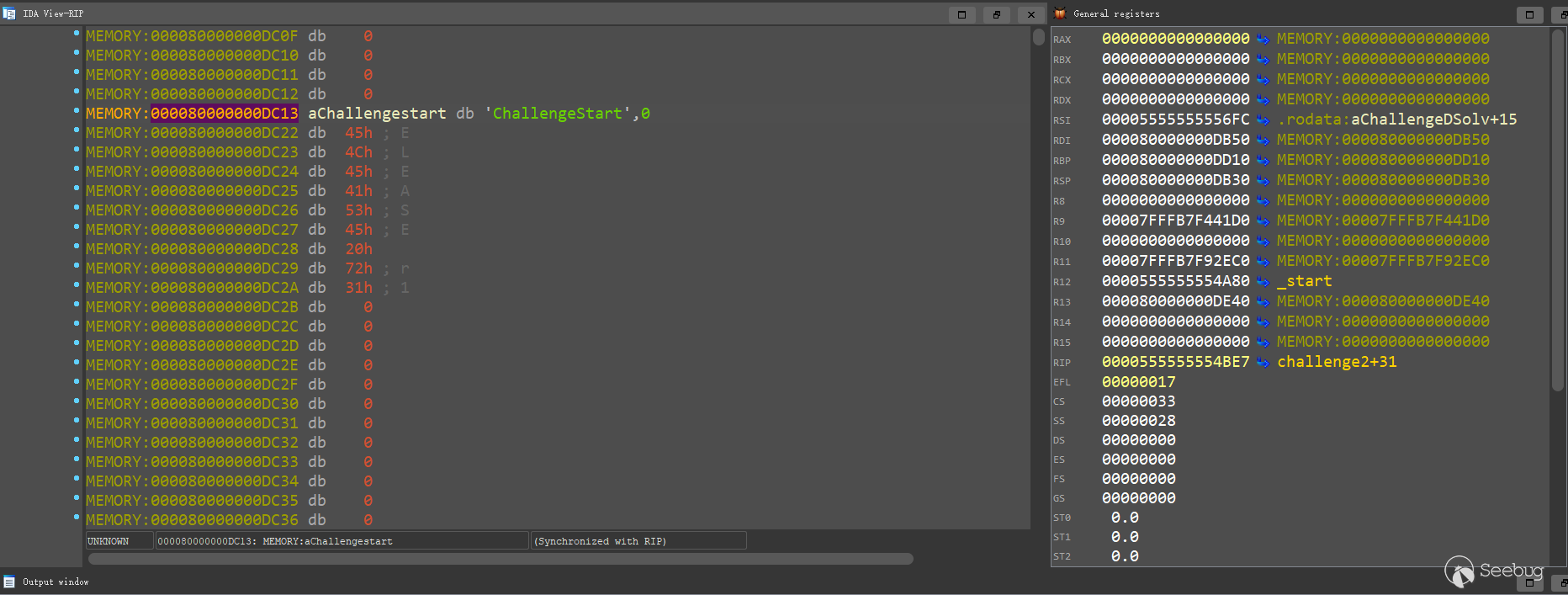
運行腳本,challenge2已解決:
Checking which challenge are solved...
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x54) = 0x54
Note: Some challenges will results in segfaults and infinite loops if they aren't solved.
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x5a) = 0x5a
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x1) = 0x1
[=] uname(buf = 0x80000000db50) = 0x0
Challenge 1: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
[=] openat(fd = 0xffffff9c, path = 0x555555555698, flags = 0x0, mode = 0x0) = -0x2 (ENOENT)
[=] read(fd = 0xffffffff, buf = 0x80000000dcc0, length = 0x20) = -0x9 (EBADF)
[=] read(fd = 0xffffffff, buf = 0x80000000dcbf, length = 0x1) = -0x9 (EBADF)
[=] close(fd = 0xffffffff) = -0x1 (EPERM)
[=] getrandom(buf = 0x80000000dce0, buflen = 0x20, flags = 0x1) = 0x20
Challenge 2: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
Challenge 3: NOT SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x18) = 0x18
[=] time() = 0x6471f7b0
Challenge 4: NOT SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x18) = 0x18Challenge 3: 自定義文件對象
Challenge 3: Make '/dev/urandom' and 'getrandom' "collide".
IDA 看一下 Challenge 3:
.text:0000555555554D31 public challenge3
.text:0000555555554D31 challenge3 proc near ; CODE XREF: start+16B↓p
.text:0000555555554D31
.text:0000555555554D31 var_68 = qword ptr -68h
.text:0000555555554D31 var_60 = dword ptr -60h
.text:0000555555554D31 var_5C = dword ptr -5Ch
.text:0000555555554D31 fd = dword ptr -58h
.text:0000555555554D31 var_51 = byte ptr -51h
.text:0000555555554D31 buf = byte ptr -50h
.text:0000555555554D31 var_30 = byte ptr -30h
.text:0000555555554D31 var_8 = qword ptr -8
.text:0000555555554D31
.text:0000555555554D31 push rbp
.text:0000555555554D32 mov rbp, rsp
.text:0000555555554D35 sub rsp, 70h
.text:0000555555554D39 mov [rbp+var_68], rdi
.text:0000555555554D3D mov rax, fs:28h
.text:0000555555554D46 mov [rbp+var_8], rax
.text:0000555555554D4A xor eax, eax
.text:0000555555554D4C mov esi, 0 ; oflag
.text:0000555555554D51 lea rdi, file ; "/dev/urandom"
.text:0000555555554D58 mov eax, 0
.text:0000555555554D5D call _open
.text:0000555555554D62 mov [rbp+fd], eax
.text:0000555555554D65 lea rcx, [rbp+buf]
.text:0000555555554D69 mov eax, [rbp+fd]
.text:0000555555554D6C mov edx, 20h ; ' ' ; nbytes
.text:0000555555554D71 mov rsi, rcx ; buf
.text:0000555555554D74 mov edi, eax ; fd
.text:0000555555554D76 call _read
.text:0000555555554D7B lea rcx, [rbp+var_51]
.text:0000555555554D7F mov eax, [rbp+fd]
.text:0000555555554D82 mov edx, 1 ; nbytes
.text:0000555555554D87 mov rsi, rcx ; buf
.text:0000555555554D8A mov edi, eax ; fd
.text:0000555555554D8C call _read
.text:0000555555554D91 mov eax, [rbp+fd]
.text:0000555555554D94 mov edi, eax ; fd
.text:0000555555554D96 call _close
.text:0000555555554D9B lea rax, [rbp+var_30]
.text:0000555555554D9F mov edx, 1
.text:0000555555554DA4 mov esi, 20h ;
.text:0000555555554DA9 mov rdi, rax
.text:0000555555554DAC call _getrandom
.text:0000555555554DB1 mov [rbp+var_60], 0
.text:0000555555554DB8 mov [rbp+var_5C], 0
.text:0000555555554DBF jmp short loc_555555554DF3
.text:0000555555554DC1 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555554DC1
.text:0000555555554DC1 loc_555555554DC1: ; CODE XREF: challenge3+C6↓j
.text:0000555555554DC1 mov eax, [rbp+var_5C]
.text:0000555555554DC4 cdqe
.text:0000555555554DC6 movzx edx, [rbp+rax+buf] ; edx清零,讀取 rbp+rax+buf 地址處的一個字節,并將其擴充到64位移入edx寄存器低8位
.text:0000555555554DCB mov eax, [rbp+var_5C]
.text:0000555555554DCE cdqe ; 將32位eax值擴展為64位rax值
.text:0000555555554DD0 movzx eax, [rbp+rax+var_30]
.text:0000555555554DD5 cmp dl, al
.text:0000555555554DD7 jnz short loc_555555554DEF
.text:0000555555554DD9 mov eax, [rbp+var_5C]
.text:0000555555554DDC cdqe
.text:0000555555554DDE movzx edx, [rbp+rax+buf]
.text:0000555555554DE3 movzx eax, [rbp+var_51]
.text:0000555555554DE7 cmp dl, al ; di:edx低8位,al:eax低8位
.text:0000555555554DE9 jz short loc_555555554DEF
.text:0000555555554DEB add [rbp+var_60], 1
.text:0000555555554DEF
.text:0000555555554DEF loc_555555554DEF: ; CODE XREF: challenge3+A6↑j
.text:0000555555554DEF ; challenge3+B8↑j
.text:0000555555554DEF add [rbp+var_5C], 1
.text:0000555555554DF3
.text:0000555555554DF3 loc_555555554DF3: ; CODE XREF: challenge3+8E↑j
.text:0000555555554DF3 cmp [rbp+var_5C], 1Fh
.text:0000555555554DF7 jle short loc_555555554DC1 ; 小于或等于則跳轉
.text:0000555555554DF9 cmp [rbp+var_60], 20h ;
.text:0000555555554DFD jnz short loc_555555554E06
.text:0000555555554DFF mov rax, [rbp+var_68]
.text:0000555555554E03 mov byte ptr [rax], 1 ; byte ptr是指定操作數的大小,這里是一個byte
; 將字節值1存儲在rax寄存器指向的內存地址中
.text:0000555555554E06
.text:0000555555554E06 loc_555555554E06: ; CODE XREF: challenge3+CC↑j
.text:0000555555554E06 nop
.text:0000555555554E07 mov rax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555554E0B xor rax, fs:28h
.text:0000555555554E14 jz short locret_555555554E1B
.text:0000555555554E16 call ___stack_chk_fail
.text:0000555555554E1B ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555554E1B
.text:0000555555554E1B locret_555555554E1B: ; CODE XREF: challenge3+E3↑j
.text:0000555555554E1B leave
.text:0000555555554E1C retn
.text:0000555555554E1C challenge3 endpChallenge 3 偽代碼:
unsigned __int64 __fastcall challenge3(_BYTE *a1)
{
int v2; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-60h]
int i; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-5Ch]
int fd; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-58h]
char v5; // [rsp+1Fh] [rbp-51h] BYREF
char buf[32]; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-50h] BYREF
char v7[40]; // [rsp+40h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v8; // [rsp+68h] [rbp-8h]
v8 = __readfsqword(0x28u); // 從fs段讀取地址0x28處的8個字節,并將其存儲在v8變量中。地址0x28處的數據通常被用來存儲函數的返回地址
fd = open("/dev/urandom", 0);
read(fd, buf, 0x20uLL);
read(fd, &v5, 1uLL);
close(fd);
getrandom(v7, 32LL, 1LL);
v2 = 0;
for ( i = 0; i <= 31; ++i )
{
if ( buf[i] == v7[i] && buf[i] != v5 )
++v2;
}
if ( v2 == 32 )
*a1 = 1; // 修改指針所指向的內存中的值
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v8;
}分析程序邏輯,主要關注點在buf,v5與v7三者之間的關系:
read(fd, buf, 0x20uLL);
read(fd, &v5, 1uLL);
···
getrandom(v7, 32LL, 1LL);read(fd, buf, 0x20uLL):從文件描述符fd讀取32(0x20)字節的數據,并將其存儲在字符數組buf中。原函數:ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
read(fd, &v5, 1uLL):從文件描述符fd讀取1字節的數據,并將其存儲在字符變量v5中。
getrandom(v7, 32LL, 1LL):系統調用,從系統提供的隨機數源獲取隨機數據。代碼含義是從系統熵池中獲取32字節的隨機數據,并將其存儲在字符數組v7中。
我們需要在i循環中讓buf[i]與v7[i]相等,且buf[i]不等于v5。getrandom是利用系統調用獲取隨機數,urandom是利用文件讀寫操作獲取隨機數,要解決這道題需要讓兩者一樣。關于 /dev/urandom 與 getrandom 的相關知識:
/dev/urandom 是一個 Unix/Linux 系統中的特殊文件,它是一個偽隨機數發生器設備文件,用于生成隨機數。
在Qiling中使用 ql.add_fs_mapper("/dev/urandom", "/dev/urandom") 將宿主機中的 /dev/urandom (后面的) 設備文件映射到 Qiling 虛擬機中的 /dev/urandom (前面的) 文件上,以便為虛擬機中的程序提供隨機數服務。
getrandom使用方法:
getrandom(ql, buf, buflen, flags)
buf:指向緩沖區的指針,用于存儲讀取到的隨機數據。
buflen:要從系統熵池讀取的字節數。
flags:指定 getrandom 函數的行為。常見的 flags 值包括:
0:如果系統熵池中沒有足夠的熵,getrandom 會阻塞直到有足夠的熵可用。
GRND_NONBLOCK(通常為 1):getrandom 在系統熵池中沒有足夠的熵時,會立即返回錯誤而不是阻塞。
GRND_RANDOM(通常為 2):嘗試從 /dev/random 獲取隨機數據,而不是從 /dev/urandom 獲取。這個選項會導致 getrandom 的行為更加謹慎,可能會在熵不足時阻塞。
返回值:
如果成功獲取隨機數據,getrandom 返回實際讀取的字節數。
如果出錯,返回 -1 并設置 errno。常見的錯誤包括 EAGAIN(系統熵池中沒有足夠的熵,且 flags 設置為非阻塞模式)和 EFAULT(buf 指針無效或指向不可訪問的內存區域)。我們可以使用
我們可以通過hook系統調用自定義一個"getrandom",例如: 運行后,可以看到challenge 3已解決: Challenge 4: Enter inside the "forbidden" loop. IDA 查看偽代碼發現什么都看不到: 根據匯編邏輯,我們最終需要實現 實際上就是 0比0,我們需要讓 我們根據邏輯patch匯編使得 可以看到我們的分析是正確的,接著就來編寫 Qiling challenge 4 writeup: 運行后,可以看到 challenge 4 已經被解決: Challenge 5: Guess every call to rand(). challenge 5 偽代碼如下: 分析代碼邏輯,我們想要最后得到 運行后沒有顯示第五個挑戰是否被解決,因為被第六題的死循環卡住了。 Challenge 6: Avoid the infinite loop. 查看偽代碼,可以看到跟第四題一樣: 我們需要執行loc_555555554F0B函數,然后再退出循環。我們需要讓ZF=0,jnz才能跳轉loc_555555554F0B函數。 主要關注點在 因此我們需要將eax設置為0,對 運行后可以看到第五個挑戰已經解決,但是第六個還沒顯示,應該是需要解出第七題: Challenge 7: Don't waste time waiting for 'sleep'. 偽代碼如下: 我們可以利用之前學的方法hook sleep函數,還是比較簡單的。 運行后,可以看到1-7題已解決: Challenge 8: Unpack the struct and write at the target address. 偽代碼如下: v2是一個指針,指向malloc分配的內存塊,相當于結構體的頭指針,結構體整理后的內容如下: 我們需要修改 運行后可以看到第八題已解出: Challenge 9: Fix some string operation to make the iMpOsSiBlE come true. 偽代碼為: 根據代碼,我們需要讓 運行后順利通過: Challenge 10: Fake the 'cmdline' line file to return the right content. 對應偽代碼為: 根據代碼,我們需要讓 buf 等于 "qilinglab"。
fd:open失敗為-1,open成功為0。
/proc/self/cmdline是一個在Linux系統中的特殊文件,它提供了當前進程(即訪問/proc/self/cmdline的進程)的命令行參數信息。 假如我們使用命令 按照第三個挑戰的方法,我們可以使用自定義文件對象來更改讀取文件時的返回值: 在運行后并沒有解題成功,好像是在hook c 程序:用來讀取cmdline,文件名:test_cmdline python程序:用來hook test_cmdline 中的文件操作 運行結果如下,可以看到確實在讀取操作的過程中存在問題。 切換到 Qilinglab當時使用的版本看一下是否存在這個問題,Qilinglab的文章是7月21發的,對應Qiling版本應該是1.2.4,使用pip指定版本安裝方法: 運行后存在版本不兼容問題,因此我將從這個版本開始直到最新版的每個版本都進行了測試。結果如下: 1.4.3 可以正確進行文件映射: 1.4.4 無法正確進行文件映射: 我們使用的最新版是 1.4.5,也就是說在1.4.3到1.4.4這個版本更新中可能存在問題,因此接下來進行代碼審計。文件映射在源碼對應的 改動如下: 第1點: 在之前,Qiling只支持字符串和對象做為文件系統映射。而QlFsMappedCallable允許用戶傳入一個類對象real_dest,然后在調用時實例化這個類對象。 用于 第2點: 第3點: 第4點: 我們替換1.4.4的mapper.py為1.4.3版本, 更改后依然沒變化,報錯。接著分析是否是針對 看一下更新對比: 1.4.4版本的linux.py文件與1.4.3版本的linux.py文件相比,有以下主要改動: 之前在1.4.3版本中模擬/proc目錄的方式有兩個: 這兩種方式存在一定缺點: 所以總的來說1.4.4版本對/proc處理做了封裝,使得它更模塊化、易用。但是在新增的幾個模塊中對 '/proc/self/auxv' 等文件做出了額外的限制,我們在映射這幾個文件時可能存在問題。因此我懷疑 cmdline 的問題就是在這個地方。 接著看run(self)函數: 這段代碼的含義是: 只有在加載ELF文件或可執行程序的時候,才設置/proc文件系統。 因此將此處判斷代碼注釋后,就應該可以成功運行了。注釋后運行: 運行成功! 這個問題應該在1.4.4和1.4.5中都存在,我們可以通過新增一個選項 修改 這樣我們只需要將ql改成下面的代碼即可: 然后修改我們的challenge10測試一下,運行成功! Challenge 11: Bypass CPUID/MIDR_EL1 checks. 偽代碼如下: 關鍵部分匯編代碼如下: 我們需要讓 因此我們跳過cpuid指令修改寄存器即可。 最后可以看到全部題目均已解決: 最后完整代碼為: 跟著上面的文章思路走一遍,我相信大家已經了解了 Qiling 框架的使用方法。通過分析 Qiling 的源碼,也加強了我對 Qiling框架的理解。 如果在本文中發現問題,歡迎大家在下面留言。 Qiling 官方文檔from qiling import Qiling
from qiling.os.mapper import QlFsMappedObject
class FakeUrandom(QlFsMappedObject):
def read(self, size: int) -> bytes:
if size == 1:
return b"\x42" # v5的長度為1
# return a constant value upon reading
else:
return b"\x41"
def fstat(self) -> int: # fstat() 是Linux/Unix系統調用之一,用來獲取文件的狀態信息
# return -1 to let syscall fstat ignore it
return -1
def close(self) -> int:
return 0
if __name__ == "__main__":
ql = Qiling([r'rootfs/x86_linux/bin/x86_fetch_urandom'], r'rootfs/x86_linux')
ql.add_fs_mapper(r'/dev/urandom', FakeUrandom())
ql.run()def hook_getrandom(ql, buf, buflen, flags):
# 自定義 getrandom 函數實現
if buflen == 32:
data = b'\x41' * buflen # b'\x41' = A
ql.mem.write(buf, data)
ql.os.set_syscall_return(buflen)
else:
ql.os.set_syscall_return(-1)
···
# 調用自定義系統調用
ql.os.set_syscall("getrandom", hook_getrandom)writeup 3
from qiling import *
from qiling.const import * #?導入Qiling模擬器中的常量
from qiling.os.mapper import QlFsMappedObject
class FakeUrandom(QlFsMappedObject):
def read(self, size: int) -> bytes:
if size == 1:
return b"\x42"
else:
return b"\x41" * size
def close(self) -> int:
return 0
def hook_getrandom(ql, buf, buflen, flags):
# 自定義 getrandom 函數實現
if buflen == 32:
data = b'\x41' * buflen # b'\x41' = A
ql.mem.write(buf, data)
ql.os.set_syscall_return(buflen)
else:
ql.os.set_syscall_return(-1)
def challenge3(ql):
ql.add_fs_mapper(r'/dev/urandom', FakeUrandom())
ql.os.set_syscall("getrandom", hook_getrandom)
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = ["rootfs/x8664_linux/qilinglab-x86_64"]
rootfs = "rootfs/x8664_linux"
ql = Qiling(path, rootfs)
# 記得加上challenge1
challenge2(ql)
ql.run()Checking which challenge are solved...
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x54) = 0x54
Note: Some challenges will results in segfaults and infinite loops if they aren't solved.
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x5a) = 0x5a
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x1) = 0x1
utsname address: 0x80000000db50
[=] uname(buf = 0x80000000db50) = 0x0
Challenge 1: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
[=] openat(fd = 0xffffff9c, path = 0x555555555698, flags = 0x0, mode = 0x0) = 0x3
[=] read(fd = 0x3, buf = 0x80000000dcc0, length = 0x20) = 0x20
[=] read(fd = 0x3, buf = 0x80000000dcbf, length = 0x1) = 0x1
[=] close(fd = 0x3) = 0x0
[=] getrandom(buf = 0x80000000dce0, buflen = 0x20, flags = 0x1) = ?
Challenge 2: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
Challenge 3: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
[=] time() = 0x6472521d
Challenge 4: NOT SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x18) = 0x18Challenge 4:hook特定地址
.text:0000555555554E1D public challenge4
.text:0000555555554E1D challenge4 proc near ; CODE XREF: start+18F↓p
.text:0000555555554E1D
.text:0000555555554E1D var_18 = qword ptr -18h
.text:0000555555554E1D var_8 = dword ptr -8
.text:0000555555554E1D var_4 = dword ptr -4
.text:0000555555554E1D
.text:0000555555554E1D push rbp
.text:0000555555554E1E mov rbp, rsp
.text:0000555555554E21 mov [rbp+var_18], rdi
.text:0000555555554E25 mov [rbp+var_8], 0
.text:0000555555554E2C mov [rbp+var_4], 0
.text:0000555555554E33 jmp short loc_555555554E40
.text:0000555555554E35 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555554E35
.text:0000555555554E35 loc_555555554E35: ; CODE XREF: challenge4+29↓j
.text:0000555555554E35 mov rax, [rbp+var_18]
.text:0000555555554E39 mov byte ptr [rax], 1
.text:0000555555554E3C add [rbp+var_4], 1
.text:0000555555554E40
.text:0000555555554E40 loc_555555554E40: ; CODE XREF: challenge4+16↑j
.text:0000555555554E40 mov eax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555554E43 cmp [rbp+var_4], eax
.text:0000555555554E46 jl short loc_555555554E35 ; 小于則跳轉
.text:0000555555554E48 nop
.text:0000555555554E49 pop rbp
.text:0000555555554E4A retn
.text:0000555555554E4A challenge4 endp__int64 challenge4()
{
return 0LL;
}mov byte ptr [rax], 1 ,但是在 loc_555555554E40 中 :mov [rbp+var_8], 0
mov [rbp+var_4], 0
···
mov eax, [rbp+var_8]
cmp [rbp+var_4], eax
add [rbp+var_4], 1[rbp+var_4]小于[rbp+var_8],jl指令才會跳轉到loc_555555554E35函數中,執行*a=1,然后再通過 add [rbp+var_4], 1 跳出循環。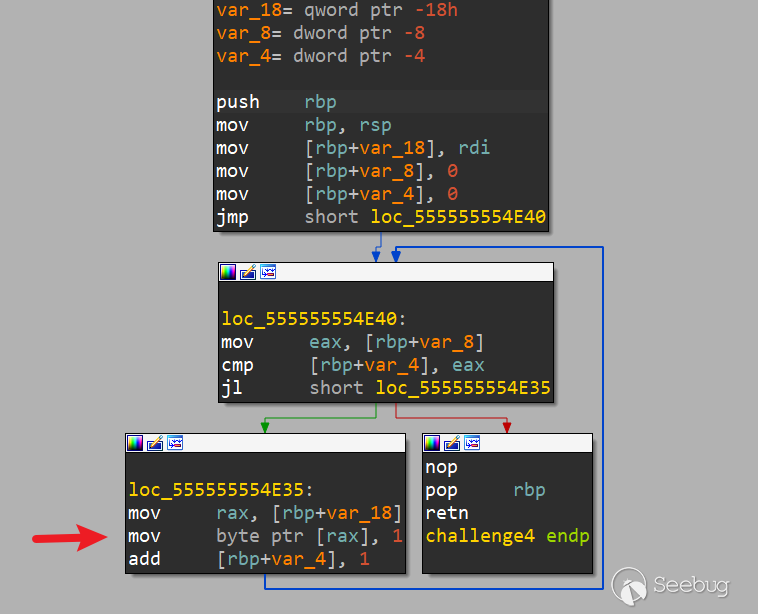
[rbp+var_8], 1 ,就可以得到正確的偽代碼: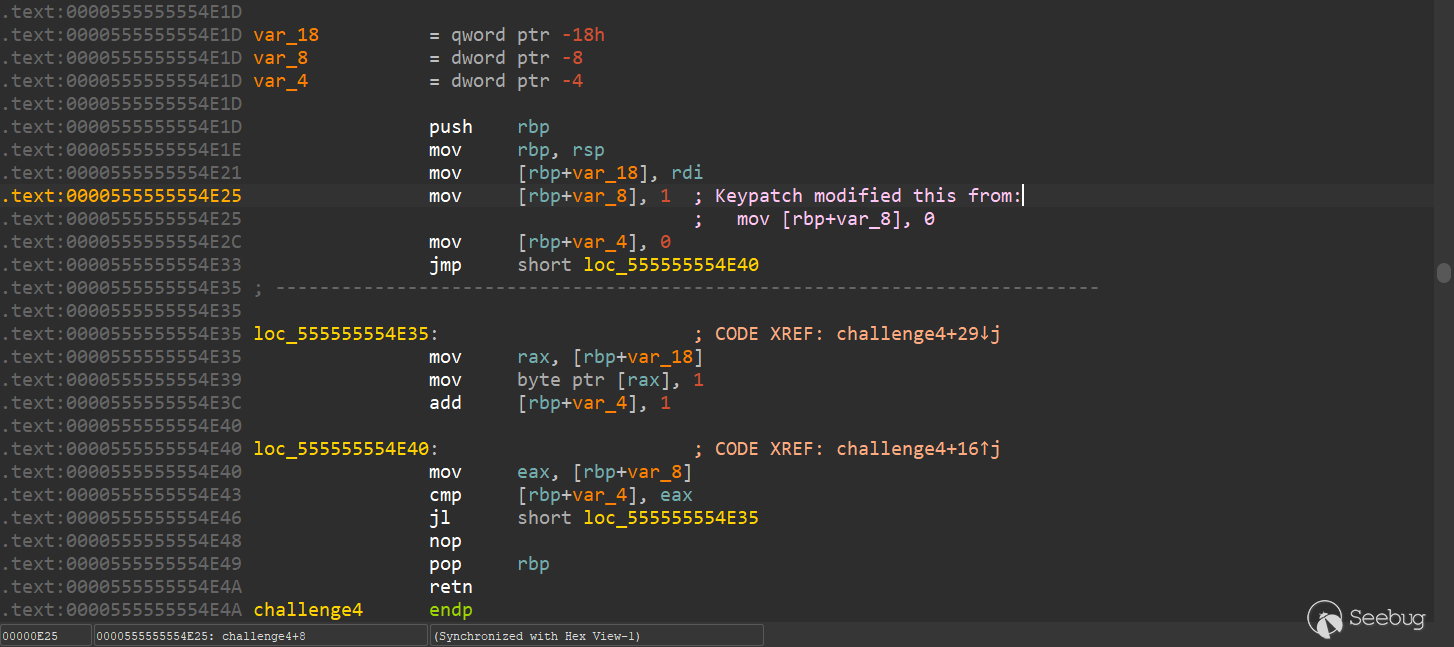
__int64 __fastcall challenge4(_BYTE *a1)
{
__int64 result; // rax
int i; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-4h]
for ( i = 0; ; ++i ) // for 循環運行一次后讓*a1 = 1,接著break。
{
result = 1LL;
if ( i >= 1 )
break;
*a1 = 1;
}
return result;
}writeup 4
def enter_forbidden_loop_hook(ql):
ql.arch.regs.eax = 1
?
def challenge4(ql):
"""
.text:0000555555554E40 mov eax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555554E43 cmp [rbp+var_4], eax <-- 在運行此命令前hook eax,使得eax = 1
.text:0000555555554E46 jl short loc_555555554E35
"""
base = ql.mem.get_lib_base(os.path.split(ql.path)[-1]) # 根據文件路徑查找已經加載的文件,獲取對應文件的基地址
# os.path.split(ql.path):os.path.split 函數將 ql.path 分成兩部分:目錄名和基本文件名。這個函數返回一個包含這兩部分的元組。
# os.path.split(ql.path)[-1]:這將返回元組中的最后一個元素,即基本文件名。在 Python 中,-1 索引表示列表或元組的最后一個元素。
# base = ql.mem.get_lib_base(os.path.split(ql.path)[-1]):ql.mem.get_lib_base 函數使用提取的文件名作為參數,以獲取已加載庫的基地址。將返回的基地址賦值給變量 base
hook_addr = base + 0xE43
ql.hook_address(enter_forbidden_loop_hook, hook_addr) # 當執行流程到達hook_addr時,該函數將被調用。此時hook_addr處的代碼還未被執行。Challenge 1: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
[=] openat(fd = 0xffffff9c, path = 0x555555555698, flags = 0x0, mode = 0x0) = 0x3
[=] read(fd = 0x3, buf = 0x80000000dcc0, length = 0x20) = 0x20
[=] read(fd = 0x3, buf = 0x80000000dcbf, length = 0x1) = 0x1
[=] close(fd = 0x3) = 0x0
[=] getrandom(buf = 0x80000000dce0, buflen = 0x20, flags = 0x1) = ?
Challenge 2: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
Challenge 3: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
[=] time() = 0x64730987
Challenge 4: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14Challenge 5:hook函數調用
.text:0000555555554E4B public challenge5
.text:0000555555554E4B challenge5 proc near ; CODE XREF: start+1B3↓p
.text:0000555555554E4B
.text:0000555555554E4B var_58 = qword ptr -58h
.text:0000555555554E4B var_48 = dword ptr -48h
.text:0000555555554E4B var_44 = dword ptr -44h
.text:0000555555554E4B var_40 = dword ptr -40h
.text:0000555555554E4B var_20 = dword ptr -20h
.text:0000555555554E4B var_8 = qword ptr -8
.text:0000555555554E4B
.text:0000555555554E4B push rbp
.text:0000555555554E4C mov rbp, rsp
.text:0000555555554E4F sub rsp, 60h
.text:0000555555554E53 mov [rbp+var_58], rdi
.text:0000555555554E57 mov rax, fs:28h
.text:0000555555554E60 mov [rbp+var_8], rax
.text:0000555555554E64 xor eax, eax
.text:0000555555554E66 mov edi, 0 ; timer
.text:0000555555554E6B call _time
.text:0000555555554E70 mov edi, eax ; seed
.text:0000555555554E72 call _srand
.text:0000555555554E77 mov [rbp+var_48], 0
.text:0000555555554E7E jmp short loc_555555554EA1
.text:0000555555554E80 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555554E80
.text:0000555555554E80 loc_555555554E80: ; CODE XREF: challenge5+5A↓j
.text:0000555555554E80 mov eax, [rbp+var_48]
.text:0000555555554E83 cdqe
.text:0000555555554E85 mov [rbp+rax*4+var_40], 0
.text:0000555555554E8D call _rand
.text:0000555555554E92 mov edx, eax
.text:0000555555554E94 mov eax, [rbp+var_48]
.text:0000555555554E97 cdqe
.text:0000555555554E99 mov [rbp+rax*4+var_20], edx
.text:0000555555554E9D add [rbp+var_48], 1
.text:0000555555554EA1
.text:0000555555554EA1 loc_555555554EA1: ; CODE XREF: challenge5+33↑j
.text:0000555555554EA1 cmp [rbp+var_48], 4
.text:0000555555554EA5 jle short loc_555555554E80
.text:0000555555554EA7 mov [rbp+var_44], 0
.text:0000555555554EAE jmp short loc_555555554ED3
.text:0000555555554EB0 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555554EB0
.text:0000555555554EB0 loc_555555554EB0: ; CODE XREF: challenge5+8C↓j
.text:0000555555554EB0 mov eax, [rbp+var_44]
.text:0000555555554EB3 cdqe
.text:0000555555554EB5 mov edx, [rbp+rax*4+var_40]
.text:0000555555554EB9 mov eax, [rbp+var_44]
.text:0000555555554EBC cdqe
.text:0000555555554EBE mov eax, [rbp+rax*4+var_20]
.text:0000555555554EC2 cmp edx, eax
.text:0000555555554EC4 jz short loc_555555554ECF
.text:0000555555554EC6 mov rax, [rbp+var_58]
.text:0000555555554ECA mov byte ptr [rax], 0
.text:0000555555554ECD jmp short loc_555555554EE0
.text:0000555555554ECF ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555554ECF
.text:0000555555554ECF loc_555555554ECF: ; CODE XREF: challenge5+79↑j
.text:0000555555554ECF add [rbp+var_44], 1
.text:0000555555554ED3
.text:0000555555554ED3 loc_555555554ED3: ; CODE XREF: challenge5+63↑j
.text:0000555555554ED3 cmp [rbp+var_44], 4
.text:0000555555554ED7 jle short loc_555555554EB0
.text:0000555555554ED9 mov rax, [rbp+var_58]
.text:0000555555554EDD mov byte ptr [rax], 1
.text:0000555555554EE0
.text:0000555555554EE0 loc_555555554EE0: ; CODE XREF: challenge5+82↑j
.text:0000555555554EE0 mov rax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555554EE4 xor rax, fs:28h
.text:0000555555554EED jz short locret_555555554EF4
.text:0000555555554EEF call ___stack_chk_fail
.text:0000555555554EF4 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555554EF4
.text:0000555555554EF4 locret_555555554EF4: ; CODE XREF: challenge5+A2↑j
.text:0000555555554EF4 leave
.text:0000555555554EF5 retn
.text:0000555555554EF5 challenge5 endpunsigned __int64 __fastcall challenge5(_BYTE *a1)
{
unsigned int v1; // eax
int i; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-48h]
int j; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-44h]
int v5[14]; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-40h]
unsigned __int64 v6; // [rsp+58h] [rbp-8h]
v6 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
v1 = time(0LL);
srand(v1); // srand 使用時間作為種子,生成真正的隨機數
for ( i = 0; i <= 4; ++i )
{
v5[i] = 0; // 0,1,2,3,4
v5[i + 8] = rand(); // 8,9,19,11,12
}
for ( j = 0; j <= 4; ++j ) // 我們需要繞過此循環
{
if ( v5[j] != v5[j + 8] )
{
*a1 = 0;
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v6;
}
}
*a1 = 1;
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v6;
}*a1 = 1的話,需要繞過第二個for循環。讓rand()得到的值都為0就可以了。hook方法在官方手冊 Hijacking OS API (POSIX) 。writeup 5
def hook_rand(ql):
ql.arch.regs.rax = 0 # 在x86-64架構中,函數的返回值通常保存在RAX寄存器中。rand函數的返回值會存儲在rax寄存器
def challenge5(ql):
ql.os.set_api('rand', hook_rand)Challenge 6:修改寄存器值
.text:0000555555554EF6 public challenge6
.text:0000555555554EF6 challenge6 proc near ; CODE XREF: start+1D7↓p
.text:0000555555554EF6
.text:0000555555554EF6 var_18 = qword ptr -18h
.text:0000555555554EF6 var_5 = byte ptr -5
.text:0000555555554EF6 var_4 = dword ptr -4
.text:0000555555554EF6
.text:0000555555554EF6 push rbp
.text:0000555555554EF7 mov rbp, rsp
.text:0000555555554EFA mov [rbp+var_18], rdi
.text:0000555555554EFE mov [rbp+var_4], 0
.text:0000555555554F05 mov [rbp+var_5], 1
.text:0000555555554F09 jmp short loc_555555554F12
.text:0000555555554F0B ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555554F0B
.text:0000555555554F0B loc_555555554F0B: ; CODE XREF: challenge6+22↓j
.text:0000555555554F0B mov [rbp+var_4], 1
.text:0000555555554F12
.text:0000555555554F12 loc_555555554F12: ; CODE XREF: challenge6+13↑j
.text:0000555555554F12 movzx eax, [rbp+var_5]
.text:0000555555554F16 test al, al ; 不修改al的內容,只更新標志位
.text:0000555555554F18 jnz short loc_555555554F0B ; ZF=0 則跳轉loc_555555554F0B函數
.text:0000555555554F1A mov rax, [rbp+var_18]
.text:0000555555554F1E mov byte ptr [rax], 1
.text:0000555555554F21 nop
.text:0000555555554F22 pop rbp
.text:0000555555554F23 retn
.text:0000555555554F23 challenge6 endpvoid challenge6()
{
while ( 1 )
;
}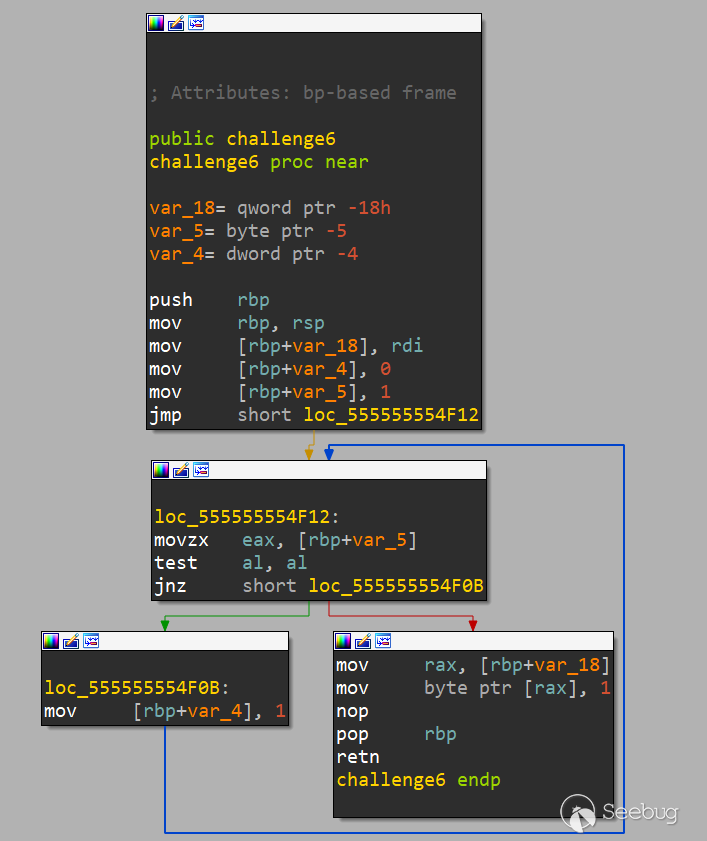
test al, al上,這條指令的含義是將EAX的低8位(al)與自身與運算,主要是用于修改ZF標志位。test al, al = al & al
由于操作數 al 相同,所以運算結果必然是 al 本身的值。
根據運算結果值是否為 0,ZF 標志位會被設置為:
結果為 0:ZF=1
結果不為 0:ZF=0mov [rbp+var_5], 1 進行patch,改為 mov [rbp+var_5], 0,就可以正確生成偽代碼了,得到的和我們預期的一致。void __fastcall challenge6(_BYTE *a1)
{
*a1 = 1;
}writeup 6
def hook_rax(ql):
ql.arch.regs.rax = 0
def challenge6(ql):
base = ql.mem.get_lib_base(os.path.split(ql.path)[-1])
hook_addr = base + 0xF16
ql.hook_address(hook_rax, hook_addr)Challenge 1: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
[=] openat(fd = 0xffffff9c, path = 0x555555555698, flags = 0x0, mode = 0x0) = 0x3
[=] read(fd = 0x3, buf = 0x80000000dcc0, length = 0x20) = 0x20
[=] read(fd = 0x3, buf = 0x80000000dcbf, length = 0x1) = 0x1
[=] close(fd = 0x3) = 0x0
[=] getrandom(buf = 0x80000000dce0, buflen = 0x20, flags = 0x1) = ?
Challenge 2: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
Challenge 3: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
[=] time() = 0x64732fa5
Challenge 4: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
Challenge 5: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14Challenge 7:hook函數調用
.text:0000555555554F24 public challenge7
.text:0000555555554F24 challenge7 proc near ; CODE XREF: start+1FB↓p
.text:0000555555554F24
.text:0000555555554F24 var_8 = qword ptr -8
.text:0000555555554F24
.text:0000555555554F24 push rbp
.text:0000555555554F25 mov rbp, rsp
.text:0000555555554F28 sub rsp, 10h
.text:0000555555554F2C mov [rbp+var_8], rdi
.text:0000555555554F30 mov rax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555554F34 mov byte ptr [rax], 1
.text:0000555555554F37 mov edi, 0FFFFFFFFh ; seconds
.text:0000555555554F3C call _sleep ; <------- hook
.text:0000555555554F41 nop
.text:0000555555554F42 leave
.text:0000555555554F43 retn
.text:0000555555554F43 challenge7 endpunsigned int __fastcall challenge7(_BYTE *a1)
{
*a1 = 1;
return sleep(0xFFFFFFFF);
}writeup 7
def hook_sleep(ql):
return 0
def challenge7(ql):
ql.os.set_api('sleep', hook_sleep)[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x19) = 0x19
You solved 7/11 of the challenges
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x22) = 0x22
[=] exit_group(code = 0x0) = ?Challenge 8:修改結構體的值
.text:0000555555554F44 public challenge8
.text:0000555555554F44 challenge8 proc near ; CODE XREF: start+21F↓p
.text:0000555555554F44
.text:0000555555554F44 var_18 = qword ptr -18h
.text:0000555555554F44 var_8 = qword ptr -8
.text:0000555555554F44
.text:0000555555554F44 push rbp
.text:0000555555554F45 mov rbp, rsp
.text:0000555555554F48 sub rsp, 20h
.text:0000555555554F4C mov [rbp+var_18], rdi
.text:0000555555554F50 mov edi, 18h ; size
.text:0000555555554F55 call _malloc
.text:0000555555554F5A mov [rbp+var_8], rax
.text:0000555555554F5E mov edi, 1Eh ; size
.text:0000555555554F63 call _malloc
.text:0000555555554F68 mov rdx, rax
.text:0000555555554F6B mov rax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555554F6F mov [rax], rdx
.text:0000555555554F72 mov rax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555554F76 mov dword ptr [rax+8], 539h
.text:0000555555554F7D mov rax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555554F81 movss xmm0, cs:dword_555555555A98
.text:0000555555554F89 movss dword ptr [rax+0Ch], xmm0
.text:0000555555554F8E mov rax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555554F92 mov rax, [rax]
.text:0000555555554F95 mov rcx, 64206D6F646E6152h
.text:0000555555554F9F mov [rax], rcx
.text:0000555555554FA2 mov dword ptr [rax+8], 617461h
.text:0000555555554FA9 mov rax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555554FAD mov rdx, [rbp+var_18]
.text:0000555555554FB1 mov [rax+10h], rdx
.text:0000555555554FB5 nop
.text:0000555555554FB6 leave
.text:0000555555554FB7 retn
.text:0000555555554FB7 challenge8 endp_DWORD *__fastcall challenge8(__int64 a1)
{
_DWORD *result; // rax
_DWORD *v2; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v2 = malloc(0x18uLL); // 調用malloc函數,請求分配0x18字節(24字節)的內存。分配成功后,指向分配內存的指針被賦值給變量v2
*(_QWORD *)v2 = malloc(0x1EuLL); // 調用malloc函數,請求分配0x1E字節(30字節)的內存。
// 將返回的指針(指向分配的30字節內存塊)存儲在v2所指向的內存中的前8個字節(64位系統一個指針大小為8字節,即一個_QWORD)
v2[2] = 1337;
v2[3] = 1039980266;
strcpy(*(char **)v2, "Random data");
result = v2;
*((_QWORD *)v2 + 2) = a1;
return result;
}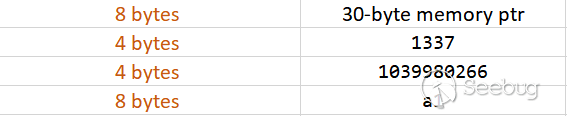
typedef struct {
char *string_ptr; // 8 字節的指針,指向字符串 "Random data" 所在的內存
uint32_t value1; // 4 字節的整數,值為 1337
uint32_t value2; // 4 字節的整數,值為 1039980266
int64_t a1; // 8 字節的整數,值為傳入的參數 a1
} CustomStruct;*a1為1,我使用的是以下方法對程序運行時存在的魔數進行搜索來判斷結構體頭指針位置,進而根據對應地址進行修改:writeup 8
import struct
def challenge8_hook(ql):
# 在內存中尋找魔數
MAGIC = 0x3DFCD6EA00000539
'''
魔數由結構體中 value1 與 value2 構成。
1. 將 value1 轉換為 16 進制表示:1337 的 16 進制表示為 0x539。
2. 將 value2 轉換為 16 進制表示:1039980266 的 16 進制表示為 0x3DFCD6EA。
3. 將 value2 字段左移 32 位,這相當于將其乘以 2^32:0x3DFCD6EA * 2^32 = 0x3DFCD6EA00000000。
4. 將 value2 與 alue1 的值相加:0x3DFCD6EA00000000 + 0x539 = 0x3DFCD6EA00000539。
所以,將 value1 和 value2 字段組合得到的魔數是 0x3DFCD6EA00000539。
'''
magic_addrs = ql.mem.search(ql.pack64(MAGIC)) # 轉換魔數成為字節序列
for magic_addr in magic_addrs: # 為了避免重復,循環檢測
# Dump and unpack the candidate structure
candidate_heap_struct_addr = magic_addr - 8 # 魔數距離堆頭指針距離為 8 bytes
candidate_heap_struct = ql.mem.read(candidate_heap_struct_addr, 24) # 獲取結構體地址結構
string_addr, _ , check_addr = struct.unpack('QQQ', candidate_heap_struct)
# struct.unpack() 是一個 Python 函數,用于將字節序列解包為多個值,解包 candidate_heap_struct 地址結構。
# 'QQQ' 是一個格式字符串,表示要解包的數據結構包含3個64位(8 字節)無符號整數。
# string_addr, _ , check_addr:只關注 string_addr 與 check_addr,最后得到相應地址
if ql.mem.string(string_addr) == "Random data":
# 修改*a1為1
ql.mem.write(check_addr, b"\x01")
break
def challenge8(ql):
base_addr = ql.mem.get_lib_base(os.path.split(ql.path)[-1])
end_of_challenge8 = base_addr + 0xFB5 # 程序運行結束時的地址
ql.hook_address(challenge8_hook, end_of_challenge8)You solved 8/11 of the challenges
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x22) = 0x22
[=] exit_group(code = 0x0) = ?Challenge 9: hook函數調用
.text:0000555555554FB8 public challenge9
.text:0000555555554FB8 challenge9 proc near ; CODE XREF: start+243↓p
.text:0000555555554FB8
.text:0000555555554FB8 var_68 = qword ptr -68h
.text:0000555555554FB8 var_58 = qword ptr -58h
.text:0000555555554FB8 dest = byte ptr -50h
.text:0000555555554FB8 src = byte ptr -30h
.text:0000555555554FB8 var_28 = qword ptr -28h
.text:0000555555554FB8 var_20 = qword ptr -20h
.text:0000555555554FB8 var_18 = dword ptr -18h
.text:0000555555554FB8 var_8 = qword ptr -8
.text:0000555555554FB8
.text:0000555555554FB8 push rbp
.text:0000555555554FB9 mov rbp, rsp
.text:0000555555554FBC sub rsp, 70h
.text:0000555555554FC0 mov [rbp+var_68], rdi
.text:0000555555554FC4 mov rax, fs:28h
.text:0000555555554FCD mov [rbp+var_8], rax
.text:0000555555554FD1 xor eax, eax
.text:0000555555554FD3 mov rax, cs:qword_5555555556A5
.text:0000555555554FDA mov rdx, cs:qword_5555555556AD
.text:0000555555554FE1 mov qword ptr [rbp+src], rax
.text:0000555555554FE5 mov [rbp+var_28], rdx
.text:0000555555554FE9 mov rax, cs:qword_5555555556B5
.text:0000555555554FF0 mov [rbp+var_20], rax
.text:0000555555554FF4 mov eax, cs:dword_5555555556BD
.text:0000555555554FFA mov [rbp+var_18], eax
.text:0000555555554FFD lea rdx, [rbp+src]
.text:0000555555555001 lea rax, [rbp+dest]
.text:0000555555555005 mov rsi, rdx ; src
.text:0000555555555008 mov rdi, rax ; dest
.text:000055555555500B call _strcpy
.text:0000555555555010 lea rax, [rbp+dest]
.text:0000555555555014 mov [rbp+var_58], rax
.text:0000555555555018 jmp short loc_555555555038
.text:000055555555501A ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:000055555555501A
.text:000055555555501A loc_55555555501A: ; CODE XREF: challenge9+89↓j
.text:000055555555501A mov rax, [rbp+var_58]
.text:000055555555501E movzx eax, byte ptr [rax]
.text:0000555555555021 movsx eax, al
.text:0000555555555024 mov edi, eax ; c
.text:0000555555555026 call _tolower
.text:000055555555502B mov edx, eax
.text:000055555555502D mov rax, [rbp+var_58]
.text:0000555555555031 mov [rax], dl
.text:0000555555555033 add [rbp+var_58], 1
.text:0000555555555038
.text:0000555555555038 loc_555555555038: ; CODE XREF: challenge9+60↑j
.text:0000555555555038 mov rax, [rbp+var_58]
.text:000055555555503C movzx eax, byte ptr [rax]
.text:000055555555503F test al, al
.text:0000555555555041 jnz short loc_55555555501A
.text:0000555555555043 lea rdx, [rbp+dest]
.text:0000555555555047 lea rax, [rbp+src]
.text:000055555555504B mov rsi, rdx ; s2
.text:000055555555504E mov rdi, rax ; s1
.text:0000555555555051 call _strcmp
.text:0000555555555056 test eax, eax
.text:0000555555555058 setz dl
.text:000055555555505B mov rax, [rbp+var_68]
.text:000055555555505F mov [rax], dl
.text:0000555555555061 nop
.text:0000555555555062 mov rax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555555066 xor rax, fs:28h
.text:000055555555506F jz short locret_555555555076
.text:0000555555555071 call ___stack_chk_fail
.text:0000555555555076 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555555076
.text:0000555555555076 locret_555555555076: ; CODE XREF: challenge9+B7↑j
.text:0000555555555076 leave
.text:0000555555555077 retn
.text:0000555555555077 challenge9 endpunsigned __int64 __fastcall challenge9(bool *a1)
{
char *i; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-58h]
char dest[32]; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-50h] BYREF
char src[40]; // [rsp+40h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v5; // [rsp+68h] [rbp-8h]
v5 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
strcpy(src, "aBcdeFghiJKlMnopqRstuVWxYz");
strcpy(dest, src);
for ( i = dest; *i; ++i )
*i = tolower(*i);
*a1 = strcmp(src, dest) == 0;
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v5;
}strcmp(src, dest) == 0 ,strcmp(str1,str2) 如果str1 == str2,則返回 0。
tolower函數是將給定的字符轉換為小寫形式。我們可以通過hook tolower讓tolower失效,strcmp自然能夠順利對比一致。writeup 9
def hook_tolower(ql):
return 0
def challenge9(ql):
ql.os.set_api('tolower', hook_tolower)You solved 9/11 of the challenges
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x22) = 0x22
[=] exit_group(code = 0x0) = ?Challenge 10:自定義文件對象
.text:0000555555555078 public challenge10
.text:0000555555555078 challenge10 proc near ; CODE XREF: start+267↓p
.text:0000555555555078
.text:0000555555555078 var_68 = qword ptr -68h
.text:0000555555555078 var_60 = dword ptr -60h
.text:0000555555555078 fd = dword ptr -5Ch
.text:0000555555555078 var_58 = qword ptr -58h
.text:0000555555555078 buf = byte ptr -50h
.text:0000555555555078 var_8 = qword ptr -8
.text:0000555555555078
.text:0000555555555078 push rbp
.text:0000555555555079 mov rbp, rsp
.text:000055555555507C sub rsp, 70h
.text:0000555555555080 mov [rbp+var_68], rdi
.text:0000555555555084 mov rax, fs:28h
.text:000055555555508D mov [rbp+var_8], rax
.text:0000555555555091 xor eax, eax
.text:0000555555555093 mov esi, 0 ; oflag
.text:0000555555555098 lea rdi, aProcSelfCmdlin ; "/proc/self/cmdline"
.text:000055555555509F mov eax, 0
.text:00005555555550A4 call _open
.text:00005555555550A9 mov [rbp+fd], eax
.text:00005555555550AC cmp [rbp+fd], 0FFFFFFFFh
.text:00005555555550B0 jz loc_55555555513F
.text:00005555555550B6 lea rcx, [rbp+buf]
.text:00005555555550BA mov eax, [rbp+fd]
.text:00005555555550BD mov edx, 3Fh ; '?' ; nbytes
.text:00005555555550C2 mov rsi, rcx ; buf
.text:00005555555550C5 mov edi, eax ; fd
.text:00005555555550C7 call _read
.text:00005555555550CC mov [rbp+var_58], rax
.text:00005555555550D0 cmp [rbp+var_58], 0
.text:00005555555550D5 jle short loc_555555555142
.text:00005555555550D7 mov eax, [rbp+fd]
.text:00005555555550DA mov edi, eax ; fd
.text:00005555555550DC call _close
.text:00005555555550E1 mov [rbp+var_60], 0
.text:00005555555550E8 jmp short loc_555555555106
.text:00005555555550EA ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:00005555555550EA
.text:00005555555550EA loc_5555555550EA: ; CODE XREF: challenge10+97↓j
.text:00005555555550EA mov eax, [rbp+var_60]
.text:00005555555550ED cdqe
.text:00005555555550EF movzx eax, [rbp+rax+buf]
.text:00005555555550F4 test al, al
.text:00005555555550F6 jnz short loc_555555555102
.text:00005555555550F8 mov eax, [rbp+var_60]
.text:00005555555550FB cdqe
.text:00005555555550FD mov [rbp+rax+buf], 20h ; ' '
.text:0000555555555102
.text:0000555555555102 loc_555555555102: ; CODE XREF: challenge10+7E↑j
.text:0000555555555102 add [rbp+var_60], 1
.text:0000555555555106
.text:0000555555555106 loc_555555555106: ; CODE XREF: challenge10+70↑j
.text:0000555555555106 mov eax, [rbp+var_60]
.text:0000555555555109 cdqe
.text:000055555555510B cmp [rbp+var_58], rax
.text:000055555555510F jg short loc_5555555550EA ; 大于則跳轉
.text:0000555555555111 lea rdx, [rbp+buf]
.text:0000555555555115 mov rax, [rbp+var_58]
.text:0000555555555119 add rax, rdx
.text:000055555555511C mov byte ptr [rax], 0
.text:000055555555511F lea rax, [rbp+buf]
.text:0000555555555123 lea rsi, s2 ; "qilinglab"
.text:000055555555512A mov rdi, rax ; s1
.text:000055555555512D call _strcmp
.text:0000555555555132 test eax, eax
.text:0000555555555134 jnz short loc_555555555143
.text:0000555555555136 mov rax, [rbp+var_68]
.text:000055555555513A mov byte ptr [rax], 1
.text:000055555555513D jmp short loc_555555555143
.text:000055555555513F ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:000055555555513F
.text:000055555555513F loc_55555555513F: ; CODE XREF: challenge10+38↑j
.text:000055555555513F nop
.text:0000555555555140 jmp short loc_555555555143
.text:0000555555555142 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555555142
.text:0000555555555142 loc_555555555142: ; CODE XREF: challenge10+5D↑j
.text:0000555555555142 nop
.text:0000555555555143
.text:0000555555555143 loc_555555555143: ; CODE XREF: challenge10+BC↑j
.text:0000555555555143 ; challenge10+C5↑j ...
.text:0000555555555143 mov rax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555555147 xor rax, fs:28h
.text:0000555555555150 jz short locret_555555555157
.text:0000555555555152 call ___stack_chk_fail
.text:0000555555555157 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000555555555157
.text:0000555555555157 locret_555555555157: ; CODE XREF: challenge10+D8↑j
.text:0000555555555157 leave
.text:0000555555555158 retn
.text:0000555555555158 challenge10 endpunsigned __int64 __fastcall challenge10(_BYTE *a1)
{
int i; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-60h]
int fd; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-5Ch]
ssize_t v4; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-58h]
char buf[72]; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-50h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v6; // [rsp+68h] [rbp-8h]
v6 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
fd = open("/proc/self/cmdline", 0);
if ( fd != -1 )
{
v4 = read(fd, buf, 0x3FuLL);
if ( v4 > 0 )
{
close(fd);
for ( i = 0; v4 > i; ++i )
{
if ( !buf[i] )
buf[i] = 32;
}
buf[v4] = 0;
if ( !strcmp(buf, "qilinglab") )
*a1 = 1;
}
}
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v6;
}./my_program arg1 arg2 arg3啟動一個程序時,讀取/proc/self/cmdline的過程在 ./my_program 中,/proc/self/cmdline文件的內容將是:./my_program\0arg1\0arg2\0arg3\0writeup 10
class Fake_cmdline(QlFsMappedObject):
def read(self, expected_len):
return b'qilinglab'
def close(self):
return 0
def challenge10(ql):
ql.add_fs_mapper('/proc/self/cmdline', Fake_cmdline())/proc/self/cmdline 這里存在問題,我寫了個腳本單獨調試以下cmdline讀取程序:#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
FILE *file;
char ch;
// 打開/proc/self/cmdline文件
file = fopen("/proc/self/cmdline", "r");
if (file == NULL) {
printf("無法打開/proc/self/cmdline文件。\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("讀取/proc/self/cmdline:\n");
// 逐個字符讀取文件內容并輸出到終端
while ((ch = fgetc(file)) != EOF) {
// 將空字符替換為換行符以提高可讀性
if (ch == '\0') {
putchar('\n');
} else {
putchar(ch);
}
}
// 關閉文件
fclose(file);
return 0;
}from qiling import *
from qiling.const import *
from qiling.os.mapper import QlFsMappedObject
from qiling.const import QL_INTERCEPT
from qiling.os.const import STRING
import struct
import os
class Fake_cmdline(QlFsMappedObject):
def read(self, expected_len):
return b'qilinglab'
def close(self):
return 0
def challenge10(ql):
ql.add_fs_mapper('/proc/self/cmdline', Fake_cmdline())
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = ["test_cmdline"]
rootfs = "rootfs/x8664_linux"
ql = Qiling(path, rootfs)
challenge10(ql)
ql.run()讀取/proc/self/cmdline:
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555555b490, count = 0x1c) = 0x1c
[=] fstat(fd = 0x3, buf_ptr = 0x80000000dc50) = -0x1 (EPERM)
[=] read(fd = 0x3, buf = 0x55555555b8a0, length = 0x2000) = 0xd
test_cmdline
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555555b490, count = 0xd) = 0xd
[=] read(fd = 0x3, buf = 0x55555555b8a0, length = 0x2000) = 0x0
[=] close(fd = 0x3) = 0x0pip install Qiling==1.2.4Challenge 10: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x15) = 0x15Challenge 10: NOT SOLVED
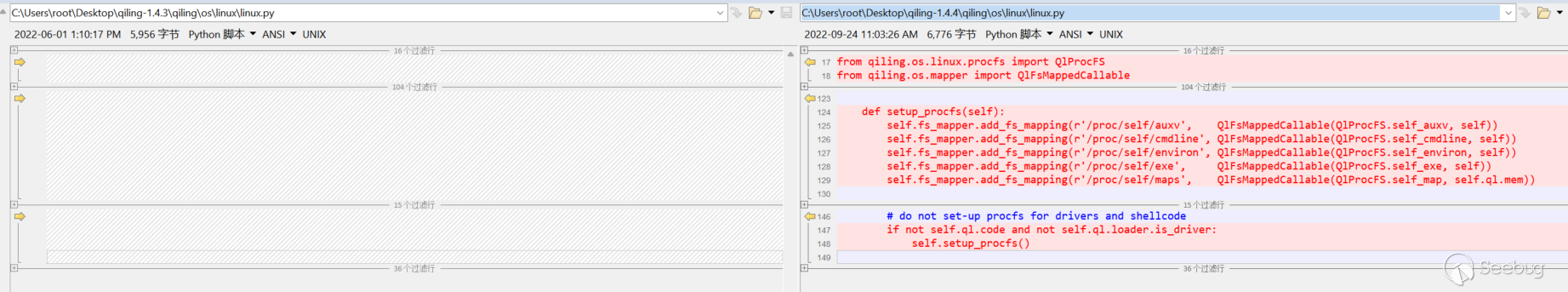
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x19) = 0x19qiling/os/mapper.py 中,我們對比一下文件改動: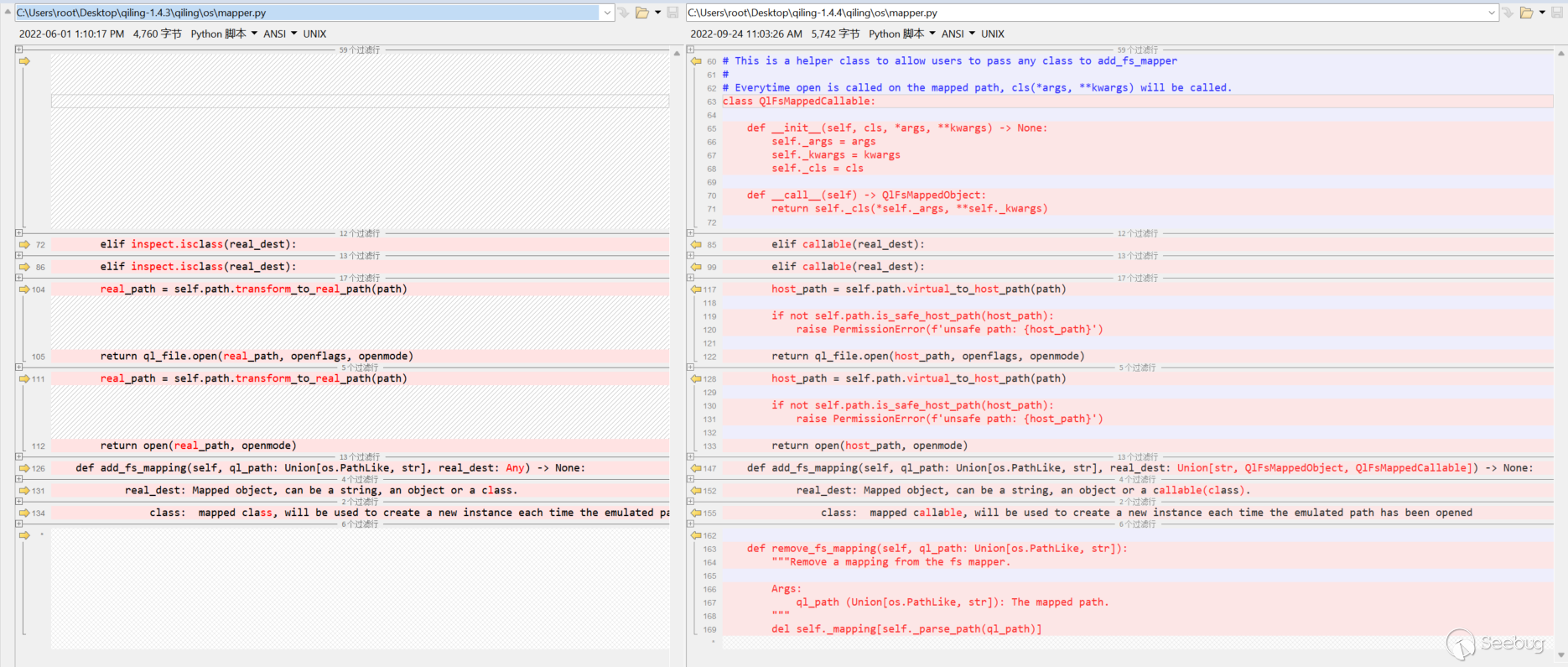
add_fs_mapping(self, ql_path: Union[os.PathLike, str], real_dest: Union[str, QlFsMappedObject, QlFsMappedCallable]) 。
vim /home/ubuntu/anaconda3/envs/ql1-4-4/lib/python3.9/site-packages/qiling/os/mapper.py/proc/self/cmdline 有新的處理方式,加載1.4.4的源碼到vscode中,發現在 linux.py 文件中新增以下代碼: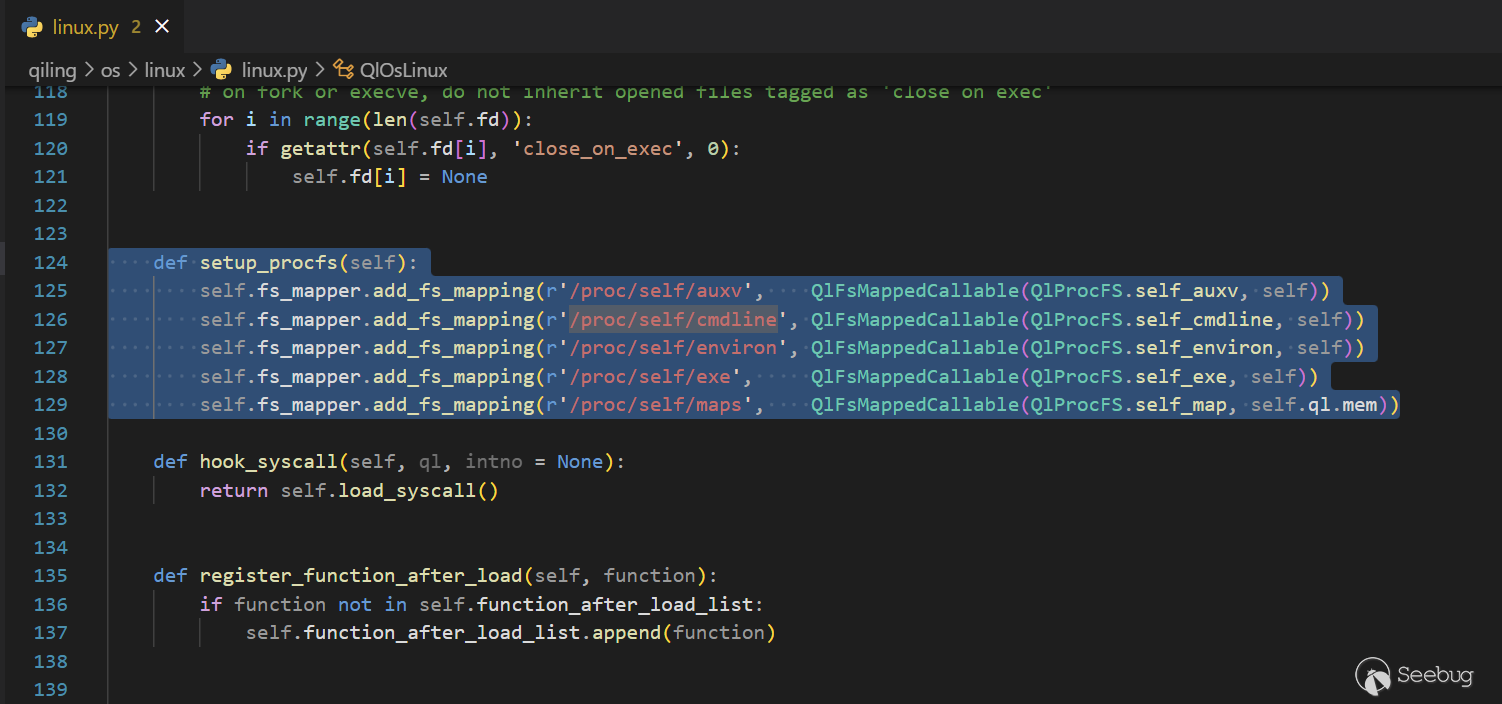
def run(self):
# do not set-up procfs for drivers and shellcode
if not self.ql.code and not self.ql.loader.is_driver:
self.setup_procfs()
self.ql.code)的情況,不設置/proc文件系統self.ql.loader.is_driver) 的情況,也不設置/proc文件系統vim /home/ubuntu/anaconda3/envs/ql1-4-4/lib/python3.9/site-packages/qiling/os/linux/linux.pyChallenge 8: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
[=] openat(fd = 0xffffff9c, path = 0x5555555556c1, flags = 0x0, mode = 0x0) = 0x3
[=] read(fd = 0x3, buf = 0x80000000dcc0, length = 0x3f) = 0x9
[=] close(fd = 0x3) = 0x0
Challenge 9: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
Challenge 10: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x15) = 0x15ql = Qiling(path, rootfs, enable_procfs=False) 來控制是否設置/proc文件系統,當enable_procfs=False 時關閉,默認值為True。我們需要修改 core.py 文件:vim /home/ubuntu/anaconda3/envs/ql1-4-4/lib/python3.9/site-packages/qiling/core.pydef __init__(
self,
argv: Sequence[str] = None,
rootfs: str = r'.',
env: MutableMapping[AnyStr, AnyStr] = {},
code: bytes = None,
ostype: Union[str, QL_OS] = None,
archtype: Union[str, QL_ARCH] = None,
verbose: QL_VERBOSE = QL_VERBOSE.DEFAULT,
profile: str = None,
console: bool = True,
log_file=None,
log_override=None,
log_plain: bool = False,
multithread: bool = False,
filter=None,
stop: QL_STOP = QL_STOP.NONE,
*,
endian: Optional[QL_ENDIAN] = None,
thumb: bool = False,
libcache: bool = False,
enable_procfs: bool = True # <---------------------------- 新添加的參數,默認值為True
):
self.enable_procfs = enable_procfs # <---------------------------- 設置 enable_procfs 屬性
······linux.py 中的代碼新增對參數enable_procfs的判斷: def run(self):
# if not self.ql.code and not self.ql.loader.is_driver: # 原來的代碼
if self.ql.enable_procfs and not self.ql.code and not self.ql.loader.is_driver:
self.setup_procfs()ql = Qiling(path, rootfs, enable_procfs=False)Challenge 8: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
[=] openat(fd = 0xffffff9c, path = 0x5555555556c1, flags = 0x0, mode = 0x0) = 0x3
[=] read(fd = 0x3, buf = 0x80000000dcc0, length = 0x3f) = 0x9
[=] close(fd = 0x3) = 0x0
Challenge 9: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x14) = 0x14
Challenge 10: SOLVED
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x15) = 0x15Challenge 11:繞過CPUID校驗
unsigned __int64 __fastcall challenge11(_BYTE *a1)
{
int v7; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-34h]
int v8; // [rsp+24h] [rbp-2Ch]
char s[4]; // [rsp+2Bh] [rbp-25h] BYREF
char v10[4]; // [rsp+2Fh] [rbp-21h] BYREF
char v11[4]; // [rsp+33h] [rbp-1Dh] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v12; // [rsp+38h] [rbp-18h]
v12 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
_RAX = 0x40000000LL;
__asm { cpuid }
v7 = _RCX;
v8 = _RDX;
if ( __PAIR64__(_RBX, _RCX) == 0x696C6951614C676ELL && (_DWORD)_RDX == 538976354 )
*a1 = 1;
sprintf(
s,
"%c%c%c%c",
(unsigned int)_RBX,
(unsigned int)((int)_RBX >> 8),
(unsigned int)((int)_RBX >> 16),
(unsigned int)((int)_RBX >> 24));
sprintf(
v10,
"%c%c%c%c",
(unsigned int)v7,
(unsigned int)(v7 >> 8),
(unsigned int)(v7 >> 16),
(unsigned int)(v7 >> 24));
sprintf(
v11,
"%c%c%c%c",
(unsigned int)v8,
(unsigned int)(v8 >> 8),
(unsigned int)(v8 >> 16),
(unsigned int)(v8 >> 24));
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v12;
}.text:000055555555518F cpuid
.text:0000555555555191 mov eax, edx
.text:0000555555555193 mov esi, ebx
.text:0000555555555195 mov [rbp+var_30], esi
.text:0000555555555198 mov [rbp+var_34], ecx
.text:000055555555519B mov [rbp+var_2C], eax
.text:000055555555519E cmp [rbp+var_30], 696C6951h
.text:00005555555551A5 jnz short loc_5555555551C0
.text:00005555555551A7 cmp [rbp+var_34], 614C676Eh
.text:00005555555551AE jnz short loc_5555555551C0
.text:00005555555551B0 cmp [rbp+var_2C], 20202062h
.text:00005555555551B7 jnz short loc_5555555551C0
.text:00005555555551B9 mov rax, [rbp+var_48]
.text:00005555555551BD mov byte ptr [rax], 1*a=1,就要讓if的判斷順利通過,if ( __PAIR64__(_RBX, _RCX) == 0x696C6951614C676ELL && (_DWORD)_RDX == 538976354 ) 的含義為:
writeup 11
def hook_cpuid(ql, address, size):
if ql.mem.read(address, size) == b'\x0F\xA2': # CPUID指令的機器碼是 0F A2
regs = ql.arch.regs
regs.ebx = 0x696C6951
regs.ecx = 0x614C676E
regs.edx = 0x20202062
regs.rip += 2 # 跳過cpuid指令防止被cpuid篡改 000055555555518F -> 0000555555555191
def challenge11(ql):
begin, end = 0, 0
for info in ql.mem.map_info:
print(info)
if info[2] == 5 and 'qilinglab-x86_64' in info[3]:
begin, end = info[:2]
print(f"{begin} -> {end}")
ql.hook_code(hook_cpuid, begin=begin, end=end)You solved 11/11 of the challenges
[=] write(fd = 0x1, buf = 0x55555575a260, count = 0x23) = 0x23
[=] exit_group(code = 0x0) = ?from qiling import *
from qiling.const import *
from qiling.os.mapper import QlFsMappedObject
from qiling.const import QL_INTERCEPT
from qiling.os.const import STRING
from qiling.os.mapper import QlFsMappedCallable
import struct
import os
def challenge1(ql):
ql.mem.map(0x1000, 0x1000, info='[challenge1]')
ql.mem.write(0x1337, ql.pack16(1337))
def my_uname_on_exit_hook(ql, *args):
rdi = ql.arch.regs.rdi
print(f"utsname address: {hex(rdi)}")
ql.mem.write(rdi, b'QilingOS\x00')
ql.mem.write(rdi + 65 * 3, b'ChallengeStart\x00')
def challenge2(ql):
ql.os.set_syscall("uname", my_uname_on_exit_hook, QL_INTERCEPT.EXIT)
class FakeUrandom(QlFsMappedObject):
def read(self, size: int) -> bytes:
if size == 1:
print("*************3**************")
return b"\x42"
else:
return b"\x41" * size
def close(self) -> int:
return 0
def hook_getrandom(ql, buf, buflen, flags):
# 自定義 getrandom 函數實現
if buflen == 32:
data = b'\x41' * buflen # b'\x41' = A
ql.mem.write(buf, data)
ql.os.set_syscall_return(buflen)
else:
ql.os.set_syscall_return(-1)
def challenge3(ql):
ql.add_fs_mapper(r'/dev/urandom', FakeUrandom())
ql.os.set_syscall("getrandom", hook_getrandom)
def enter_forbidden_loop_hook(ql):
ql.arch.regs.eax = 1
def challenge4(ql):
"""
.text:0000555555554E40 mov eax, [rbp+var_8]
.text:0000555555554E43 cmp [rbp+var_4], eax <-- 在運行此命令前hook eax,使得eax = 1
.text:0000555555554E46 jl short loc_555555554E35
"""
base = ql.mem.get_lib_base(os.path.split(ql.path)[-1]) # 根據文件路徑查找已經加載的文件,獲取對應文件的基地址
hook_addr = base + 0xE43
ql.hook_address(enter_forbidden_loop_hook, hook_addr) # 當執行流程到達hook_addr時,該函數將被調用。此時hook_addr處的代碼還未被執行。
def hook_rand(ql):
ql.arch.regs.rax = 0
def challenge5(ql):
ql.os.set_api('rand', hook_rand)
def hook_rax(ql):
ql.arch.regs.rax = 0
def challenge6(ql):
base = ql.mem.get_lib_base(os.path.split(ql.path)[-1])
hook_addr = base + 0xF16
ql.hook_address(hook_rax, hook_addr)
def hook_sleep(ql):
return 0
def challenge7(ql):
ql.os.set_api('sleep', hook_sleep)
def challenge8_hook(ql):
# Find all occurrences of the magic in memory
MAGIC = 0x3DFCD6EA00000539
magic_addrs = ql.mem.search(ql.pack64(MAGIC))
for magic_addr in magic_addrs:
# Dump and unpack the candidate structure
candidate_heap_struct_addr = magic_addr - 8
candidate_heap_struct = ql.mem.read(candidate_heap_struct_addr, 24)
string_addr, _ , check_addr = struct.unpack('QQQ', candidate_heap_struct)
# struct.unpack() 是一個 Python 函數,用于將字節序列解包為多個值,解包 candidate_heap_struct 變量中的數據。
# 'QQQ' 是一個格式字符串,表示要解包的數據結構包含3個64位(8 字節)無符號整數。
# string_addr, _ , check_addr:只關注 string_addr 與 check_addr
if ql.mem.string(string_addr) == "Random data":
# 修改*a1為1
ql.mem.write(check_addr, b"\x01")
break
def challenge8(ql):
base_addr = ql.mem.get_lib_base(os.path.split(ql.path)[-1])
end_of_challenge8 = base_addr + 0xFB5 # 程序運行結束時的地址
ql.hook_address(challenge8_hook, end_of_challenge8)
def hook_tolower(ql):
return 0
def challenge9(ql):
ql.os.set_api('tolower', hook_tolower)
class Fake_cmdline(QlFsMappedObject):
def read(self, expected_len):
return b'qilinglab'
def close(self):
return 0
def challenge10(ql):
# ql.add_fs_mapper('/proc/self/cmdline', Fake_cmdline())
ql.add_fs_mapper('/proc/self/cmdline', QlFsMappedCallable(Fake_cmdline))
def hook_cpuid(ql, address, size):
if ql.mem.read(address, size) == b'\x0F\xA2':
regs = ql.arch.regs
regs.ebx = 0x696C6951
regs.ecx = 0x614C676E
regs.edx = 0x20202062
regs.rip += 2
def challenge11(ql):
begin, end = 0, 0
for info in ql.mem.map_info:
print(info)
if info[2] == 5 and 'qilinglab-x86_64' in info[3]:
begin, end = info[:2]
print(f"{begin} -> {end}")
ql.hook_code(hook_cpuid, begin=begin, end=end)
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = ["rootfs/x8664_linux/qilinglab-x86_64"]
rootfs = "rootfs/x8664_linux"
ql = Qiling(path, rootfs, enable_procfs=False)
challenge1(ql)
challenge2(ql)
challenge3(ql)
challenge4(ql)
challenge5(ql)
challenge6(ql)
challenge7(ql)
challenge8(ql)
challenge9(ql)
challenge10(ql)
challenge11(ql)
ql.run()總結
參考文章
Qiling lab
Qiling Framework入門,11個挑戰快速上手@PJXRocks
淺嘗qiling框架-qilinglab writeup@badmonkey
11個小挑戰,Qiling Framework 入門上手跟練@Cr0ssx2
 本文由 Seebug Paper 發布,如需轉載請注明來源。本文地址:http://www.bjnorthway.com/2073/
本文由 Seebug Paper 發布,如需轉載請注明來源。本文地址:http://www.bjnorthway.com/2073/


暫無評論